RULES AND REGULATIONS
Title 25—ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION
ENVIRONMENTAL QUALITY BOARD
[ 25 PA. CODE CHS. 121, 129 AND 130 ]
Adhesives, Sealants, Primers and Solvents
[40 Pa.B. 7340]
[Saturday, December 25, 2010]The Environmental Quality Board (Board) amends Chapters 121 and 129 (relating to general provisions; and standards for sources) and adds Subchapter D (relating to adhesives, sealants, primers and solvents) to Chapter 130 (relating to standards for products), to read as set forth in Annex A.
The final-form rulemaking adds definitions to § 121.1 (relating to definitions) for 57 new terms, including those that relate to the adhesive, sealant, primer and solvent product categories that will be regulated under § 129.77 (relating to control of emissions from the use or application of adhesives, sealants, primers and solvents) and Chapter 130, Subchapter D, and amends definitions for 9 existing terms to provide clarity.
The final-form rulemaking amends § 129.51(a) (relating to general) to add § 129.77 to the list of sections for which compliance may be achieved by alternative methods.
The final-form rulemaking adds § 129.77 to regulate the owner or operator of a facility or stationary source that uses or applies, on or after January 1, 2012, a regulated adhesive, sealant, adhesive primer or sealant primer product. The final-form rulemaking adopts emission standards and volatile organic compound (VOC) content limits for the industrial or commercial use or application of 37 categories of adhesive, sealant, adhesive primer or sealant primer products, and adhesive or sealant products applied to particular substrates. The final-form rulemaking also includes requirements for the use of surface preparation solvents and cleanup solvents. Owners and operators using noncomplying products have the option to use add-on controls as a compliance alternative rather than switching to complying products.
The final-form rulemaking adds Chapter 130, Subchapter D to adopt emission standards and VOC content limits for the sale, supply, offer for sale, manufacture, use or application of 37 categories of adhesive, sealant, adhesive primer and sealant primer products; adhesive and sealant products applied to certain substrates; and surface preparation solvents and cleanup solvents. Chapter 130, Subchapter D applies to a person who, on or after January 1, 2012, sells, supplies, offers for sale or manufactures for sale an adhesive, sealant, adhesive primer, sealant primer, surface preparation solvent or cleanup solvent product for industrial or commercial use or application in this Commonwealth. The requirements also apply to a person who uses or applies in this Commonwealth, for compensation, an adhesive, sealant, adhesive primer or sealant primer product; adhesive or sealant products applied to particular substrates; or surface preparation solvent or cleanup solvent products.
This order was adopted by the Board at its meeting on September 21, 2010.
A. Effective Date
This final-form rulemaking will be effective upon publication in the Pennsylvania Bulletin.
B. Contact Persons
For further information, contact Arleen Shulman, Chief, Division of Air Resource Management, P. O. Box 8468, Rachel Carson State Office Building, Harrisburg, PA 17105-8468, (717) 772-3436; or Kristen Furlan, Assistant Counsel, Bureau of Regulatory Counsel, P. O. Box 8464, Rachel Carson State Office Building, Harrisburg, PA 17105-8464, (717) 787-7060. Persons with a disability may use the Pennsylvania AT&T Relay Service, (800) 654-5984 (TDD users) or (800) 654-5988 (voice users). This final-form rulemaking is available through the Department of Environmental Protection's (Department) web site at www.depweb.state.pa.us (Keyword: Public Participation).
C. Statutory Authority
This final-form rulemaking is authorized under section 5 of the Air Pollution Control Act (35 P. S. § 4005), which in subsection (a)(1) grants the Board the authority to adopt rules and regulations for the prevention, control, reduction and abatement of air pollution in this Commonwealth, and which in subsection (a)(8) grants the Board the authority to adopt rules and regulations designed to implement the Clean Air Act (CAA) (42 U.S.C.A. §§ 7401—7671q).
D. Background and Purpose
The purpose of this final-form rulemaking is to establish a program to limit the emissions of VOCs from the industrial and commercial use and application of certain adhesive, sealant, adhesive primer and sealant primer products; adhesive and sealant products applied to certain substrates; and surface preparation solvent and cleanup solvent products. This final-form rulemaking also extends these product requirements to the owners or operators of facilities that use these products as part of a manufacturing process and provides them with an alternative compliance method of using add-on air pollution controls in place of complying products. VOCs are a precursor for ozone formation. Ground-level ozone is not emitted directly by adhesives, sealants, primers and solvents to the atmosphere, but is formed by a photochemical reaction between VOCs and nitrogen oxides in the presence of sunlight.
The United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) is responsible for establishing National Ambient Air Quality Standards (NAAQS) for six criteria pollutants considered harmful to public health and the environment: ozone, particulate matter, nitrogen oxides, carbon monoxide, sulfur dioxide and lead. The CAA established two types of NAAQS: primary standards, limits set to protect public health; and secondary standards, limits set to protect public welfare, including protection against visibility impairment and from damage to animals, crops, vegetation and buildings. The EPA established primary and secondary ozone NAAQS to protect public health and welfare.
When ground-level ozone is present in concentrations in excess of the Federal health-based 8-hour NAAQS for ozone, public health and welfare are adversely affected. Ozone exposure correlates to increased respiratory disease and higher mortality rates. Ozone can inflame and damage the lining of the lungs. Within a few days, the damaged cells are shed and replaced. Over a long-time period, lung tissue may become permanently scarred, resulting in permanent loss of lung function and a lower quality of life. When ambient ozone levels are high, more people with asthma have attacks that require a doctor's attention or use of medication. Ozone also makes people more sensitive to allergens including pet dander, pollen and dust mites, all of which can trigger asthma attacks.
The EPA concluded that there is an association between high levels of ambient ozone and increased hospital admissions for respiratory ailments including asthma. While children, the elderly and those with respiratory problems are most at risk, even healthy individuals may experience increased respiratory ailments and other symptoms when they are exposed to high levels of ambient ozone while engaged in activities that involve physical exertion. High levels of ozone also affect animals in ways similar to humans.
In addition to causing adverse human and animal health effects, the EPA concluded that ozone affects vegetation and ecosystems, leading to reductions in agricultural crop and commercial forest yields by destroying chlorophyll; reduced growth and survivability of tree seedlings; and increased plant susceptibility to disease, pests and other environmental stresses, including harsh weather. In long-lived species, these effects may become evident only after several years or even decades and have the potential for long-term adverse impacts on forest ecosystems. Ozone damage to the foliage of trees and other plants can decrease the aesthetic value of ornamental species used in residential landscaping, as well as the natural beauty of parks and recreation areas. Through deposition, ground-level ozone also contributes to pollution in the Chesapeake Bay. The economic value of some welfare losses due to ozone can be calculated, such as crop yield loss from both reduced seed production and visible injury to some leaf crops, including lettuce, spinach and tobacco, as well as visible injury to ornamental plants, including grass, flowers and shrubs. Other types of welfare loss may not be quantifiable, such as the reduced aesthetic value of trees growing in heavily visited parks.
High levels of ground-level ozone can also cause damage to buildings and synthetic fibers, including nylon, and reduced visibility on roadways and in natural areas. The implementation of additional measures to address ozone air quality nonattainment in this Commonwealth is necessary to protect the public health and welfare, animal and plant health and welfare and the environment.
In July 1997, the EPA established primary and secondary ozone standards at a level of 0.08 part per million (ppm) averaged over 8 hours. See 62 FR 38855 (July 18, 1997). In 2004, the EPA designated 37 counties in this Commonwealth as 8-hour ozone nonattainment areas for the 1997 8-hour ozone NAAQS. This Commonwealth is meeting the 1997 standard in all areas except the five-county Philadelphia area. The areas in which the 1997 standard has been attained are required to have permanent and enforceable control measures to ensure violations do not occur for the next decade.
Furthermore, in March 2008, the EPA lowered the standard to 0.075 ppm averaged over 8 hours to provide even greater protection for children, other at-risk populations and the environment against the array of ozone-induced adverse health and welfare effects. See 73 FR 16436 (March 27, 2008). The EPA is reconsidering the March 2008 ozone NAAQS and proposed at 75 FR 2938 (January 19, 2010) to set a more protective 8-hour ozone primary standard between 0.060 and 0.070 ppm to provide increased protection for children and other at-risk groups. The EPA also proposed that the secondary ozone standard, which was set identically to the revised primary standard in the 2008 final rule, should instead be a new cumulative, seasonal standard. See 75 FR 2938. This seasonal standard is designed to protect plants and trees from damage occurring from repeated ozone exposure, which can reduce tree growth, damage leaves and increase susceptibility to disease. The final revised ozone NAAQS is expected in 2011.
There are no Federal limits for the larger container sizes of adhesive, sealant, adhesive primer and sealant primer products subject to regulation under this final-form rulemaking. The staff of the Ozone Transport Commission (OTC) and member states and the District of Columbia formed a workgroup to discuss control measures for the sale, offer for sale, supply, manufacture, industrial use and commercial application of solvent-based adhesives, sealants and primers during a series of conference calls and workshops held from the Spring of 2004 through the Autumn of 2006. The OTC workgroup collected and evaluated information regarding emission benefits, cost-effectiveness and implementation issues.
This final-form rulemaking is based on emission reduction measures recommended by the OTC in its 2006 Model Rule for adhesives, sealants and primers, which is based on the 1998 reasonably available control technology (RACT) and best available retrofit control technology (BARCT) determination by the California Air Resources Board (CARB) for the industrial and commercial use and application of adhesives, sealants and primers. The Department has reviewed the OTC 2006 Model Rule and the CARB RACT/BARCT for their applicability to the ozone reduction measures necessary for this Commonwealth.
The OTC workgroup received comments on the 2006 Model Rule from the National Paint and Coatings Association, the Adhesive and Sealant Council, Inc. and LORD Corporation. The Department reviewed these comments for applicability to the development of this Common- wealth-specific final-form rulemaking.
The Department has determined that the measures provided in the 2006 Model Rule are appropriate to be implemented in this Commonwealth.
This final-form rulemaking will assist in reducing VOC emissions locally as well as reducing the transport of VOC emissions and ground-level ozone to downwind states. This final-form rulemaking is consistent with regulatory initiatives that will be undertaken by other jurisdictions in the Ozone Transport Region (OTR). Adoption of VOC emission requirements for adhesives, sealants, primers and solvents is part of the Commonwealth's strategy, in concert with other OTR jurisdictions, to further reduce transport of VOC ozone precursors and ground-level ozone throughout the OTR to attain and maintain the 8-hour ozone NAAQS. The final-form rulemaking is reasonably necessary to attain and maintain the health-based 8-hour ozone NAAQS. This final-form rulemaking will be submitted to the EPA as a revision to the State Implementation Plan (SIP).
The final-form rulemaking was discussed with the Air Quality Technical Advisory Committee (AQTAC) on November 18, 2009, and February 18, 2010. The AQTAC unanimously concurred with the Department's recommendation to present the final-form amendments to the Board for approval for publication as a final regulation. The Department also consulted with the Citizens Advisory Council (CAC) on December 16, 2009, and the Small Business Compliance Advisory Committee (SBCAC) on July 28, 2010. Neither the CAC nor the SBCAC had concerns.
E. Summary of Regulatory Requirements; and Changes to the Proposed Rulemaking
This final-form rulemaking amends the following definitions in § 121.1 of the following terms to improve clarity, style and format or explain new product categories: ''adhesive,'' ''adhesive primer,'' ''aerospace vehicle or component,'' ''as applied,'' ''as supplied,'' ''cyanoacrylate adhesive,'' ''exempt compound or exempt solvent,'' ''sealant'' and ''solvent.''
This final-form rulemaking adds definitions in § 121.1 for the following terms to explain new product categories: ''ABS welding adhesive or acrylonitrile-butadiene-styrene welding adhesive,'' ''aerosol adhesive,'' ''architectural sealant or primer,'' ''automotive glass adhesive primer,'' ''CPVC plastic or chlorinated polyvinyl chloride plastic,'' ''CPVC welding adhesive or chlorinated polyvinyl chloride welding adhesive,'' ''ceramic tile installation adhesive,'' ''cleanup solvent,'' ''computer diskette jacket manufacturing adhesive,'' ''contact bond adhesive,'' ''cove base,'' ''cove base installation adhesive,'' ''diluent,'' ''drywall installation,'' ''fiberglass,'' ''flexible vinyl,'' ''indoor floor covering installation adhesive,'' ''laminate,'' ''low-solids adhesive, sealant or primer,'' ''marine deck sealant or marine deck sealant primer,'' ''medical equipment manufacturing,'' ''metal to urethane/rubber molding or casting adhesive,'' ''multipurpose construction adhesive,'' ''nonmembrane roof installation/repair adhesive,'' ''outdoor floor covering installation adhesive,'' ''PVC plastic or polyvinyl chloride plastic,'' ''PVC welding adhesive or polyvinyl chloride welding adhesive,'' ''panel installation,'' ''perimeter bonded sheet flooring installation,'' ''plastic cement welding adhesive,'' ''plastic cement welding adhesive primer,'' ''plastic foam,'' ''plasticizer,'' ''plastics,'' ''porous material,'' ''propellant,'' ''reactive diluent,'' ''roadway sealant,'' ''rubber,'' ''SCAQMD-South Coast Air Quality Management District,'' ''sealant primer,'' ''sheet rubber installation,'' ''single-ply roof membrane,'' ''single-ply roof membrane adhesive primer,'' ''single-ply roof membrane installation and repair adhesive,'' ''single-ply roof membrane sealant,'' ''structural glazing adhesive,'' ''subfloor installation,'' ''surface preparation solvent,'' ''thin metal laminating adhesive,'' ''tire repair,'' ''tire tread adhesive,'' ''traffic marking tape,'' ''traffic marking tape adhesive primer,'' ''undersea-based weapons systems components'' and ''waterproof resorcinol glue.''
Three of the definitions previously listed are amended in the final-form rulemaking in response to public comment: ''metal to urethane/rubber molding or casting adhesive,'' ''rubber'' and ''single-ply roof membrane.'' A fourth definition, ''fiberglass,'' is amended to include both the proposed definition and a different definition of the same term adopted at 40 Pa.B. 3328 (June 19, 2010) for a different purpose. The definition specifies which definition applies when.
The final-form rulemaking amends § 129.51(a) to extend its coverage to adhesives, sealants, primers and solvents covered by § 129.77. Section 129.51(a) provides an alternative method for owners and operators of facilities to achieve compliance with air emission limits.
The final-form rulemaking adds § 129.77. Many of the revisions to the proposed language are made for the purpose of clarity. The compliance date is also changed, based on the anticipated publication date of the final-form rulemaking.
Section 129.77(a) establishes that this section applies to the owner or operator of a facility that uses or applies at the facility, on or after January 1, 2012, an adhesive, sealant, adhesive primer or sealant primer subject to the VOC content limits in § 129.77, Table V (relating to VOC content limits for adhesives, sealants, adhesive primers and sealant primers, as applied); an adhesive or sealant product applied to the listed substrate subject to the VOC content limits in § 129.77, Table VI (relating to VOC content limits for adhesive or sealant products applied to particular substrates, as applied); or a surface preparation solvent or cleanup solvent.
Section 129.77(b) establishes that, on or after January 1, 2012, an owner or operator of a facility may not use or apply at the facility an adhesive, sealant, adhesive primer or sealant primer that exceeds the applicable VOC content limit in Table V or VI, except as provided elsewhere in § 129.77.
Section 129.77(c) establishes that, on or after January 1, 2012, an owner or operator of a facility may not use or apply at the facility a surface preparation or cleanup solvent that exceeds the applicable VOC content limit or composite vapor pressure requirements of this section, except as provided elsewhere in this section.
Section 129.77(d) specifies that the VOC content limits in Table VI apply if the adhesive or sealant does not have a VOC content limit in Table V. This subsection also specifies that if an owner or operator of a facility uses or applies at the facility an adhesive to bond dissimilar substrates together, the applicable substrate category with the highest VOC content is the limit for this use.
Section 129.77(e) specifies requirements for an owner or operator of a facility using or applying a surface preparation solvent or cleanup solvent at the facility.
Section 129.77(f) specifies the requirements for removal of an adhesive, sealant, adhesive primer or sealant primer from the parts of spray application equipment.
Section 129.77(g) addresses the requirements for an owner or operator of a facility using or applying at the facility an adhesive, sealant, adhesive primer, sealant primer, surface preparation solvent or cleanup solvent subject to this section that wants to use add-on air pollution control equipment to comply. The subsection is amended in the final-form rulemaking to add requirements for recording and maintaining daily records of certain information for add-on air pollution control devices. The final-form rulemaking also amends this subsection to provide an owner or operator of a facility that intends to comply with § 129.77 through the use of add-on air pollution control equipment with the option to request an extension to the compliance date.
Section 129.77(h) establishes that an owner or operator of a facility subject to this section shall store or dispose of all absorbent materials, including cloth or paper, which are moistened with products subject to this section, in nonabsorbent containers at the facility that are kept closed except when placing materials in or removing materials from the container.
Section 129.77(i) establishes that an owner or operator of a facility subject to this section may not solicit, require or specify the use or application of a product subject to this section if the use or application would result in a violation of this section. The final-form rulemaking clarifies that this restriction does not apply if the emissions are controlled through the use of add-on air pollution control equipment. The final-form rulemaking specifies that the prohibition of subsection (i) applies to all written or oral contracts created on or after January 1, 2012, under which an adhesive, sealant, adhesive primer, sealant primer, surface preparation solvent or cleanup solvent subject to this section is to be used or applied at a facility in this Commonwealth.
Section 129.77(j) specifies that an owner or operator of a facility subject to this section who uses or applies a product subject to this section may not add solvent to the adhesive, sealant, adhesive primer or sealant primer in an amount in excess of the manufacturer's recommendation for application, if this additional solvent causes the product to exceed the applicable VOC content limit listed in Table V or VI, unless the emissions are controlled through the use of add-on air pollution control equipment as specified in subsection (g).
Section 129.77(k) provides for certain exemptions, including exemptions for products being tested or evaluated in a research and development, quality assurance or analytical laboratory, if records are maintained as required in subsections (p) and (q); products that are subject to § 129.73 (relating to aerospace manufacturing and rework), Chapter 130, Subchapter B (relating to consumer products) or Chapter 130, Subchapter C (relating to architectural and industrial maintenance coatings); adhesives and sealants that contain less than 20 grams of VOC per liter of adhesive or sealant, less water and less exempt compounds, as applied; cyanoacrylate adhesives; adhesives, sealants, adhesive primers or sealant primers that are sold or supplied by the manufacturer or supplier in containers with a net volume of 16 fluid ounces or less, or a net weight of 1 pound or less, except plastic cement welding adhesives and contact adhesives; and contact adhesives that are sold or supplied by the manufacturer or supplier in containers with a net volume of 1 gallon or less.
Section 129.77(l) provides exemptions for the use of adhesives, sealants, adhesive primers, sealant primers, surface preparation solvents and cleanup solvents in certain operations, including tire repair operations, if the label of the tire repair adhesive states ''For tire repair only;'' the assembly, repair and manufacture of aerospace components or undersea-based weapon systems; the manufacture of medical equipment; and certain plaque laminating operations.
The final-form rulemaking deletes proposed § 129.77(m), which provided a phased-in compliance schedule for the use and application of single-ply roof membrane materials. The proposed schedule is removed because the change in compliance date to January 1, 2012, made it unnecessary.
Section 129.77(m) in the final-form rulemaking, which amends proposed § 129.77(n), provides an exemption from § 129.77 if the total VOC emissions from all adhesives, sealants, adhesive primers and sealant primers used or applied at the facility are less than 200 pounds or an equivalent volume per calendar year. An owner or operator of a facility claiming exemption under this subsection shall record and maintain operational records sufficient to demonstrate compliance with this exemption.
Section 129.77(n) in the final-form rulemaking, which amends proposed § 129.77(o), provides an exemption from § 129.77 for the use or application of a noncomplying adhesive, sealant, adhesive primer, sealant primer, surface preparation solvent or cleanup solvent if the total volume of noncomplying products used or applied facility-wide does not exceed 55 gallons per calendar year. An owner or operator of a facility claiming exemption under this subsection shall record and maintain operational records sufficient to demonstrate compliance with this exemption.
Section 129.77(o) in the final-form rulemaking, which amends proposed § 129.77(p), specifies that each owner or operator subject to this section shall maintain records demonstrating compliance with this section. This subsection is amended in the final-form rulemaking in response to comments to specify that records of volume must indicate monthly volume.
Section 129.77(p) in the final-form rulemaking, which amends proposed § 129.77(q), provides recordkeeping requirements for the person conducting testing on products that are subject to the laboratory testing exemption.
Section 129.77(q) in the final-form rulemaking, which amends proposed § 129.77(r), specifies that all records made to determine compliance with this section shall be maintained onsite for 5 years from the date the record is created and made available to the Department upon request. This subsection is amended in the final-form rulemaking in response to comments to specify that records must be made available to the Department upon receipt of a written request.
Section 129.77(r) in the final-form rulemaking, which amends proposed § 129.77(s), specifies, with certain exceptions, that the VOC and solids content of nonaerosol adhesives, sealants, adhesive primers, sealant primers, surface preparation solvents and cleanup solvents shall be determined using either EPA Reference Method 24 or South Coast Air Quality Management District (SCAQMD) Method 304, including updates and revisions. This subsection is amended in the final-form rulemaking in response to comment to specify that the VOC and solids content of nonaerosol adhesives, including one-part moisture cure urethane adhesives and silicone adhesives, shall be determined using either EPA Reference Method 24 or SCAQMD Method 304, including updates and revisions.
Section 129.77(s), added in response to public comment, adds a test method for determining the volatile matter and solids content of one-part or multiple part reactive adhesives, except one-part moisture cure urethane adhesives and silicone adhesives.
Section 129.77(t) specifies that the identity and concentration of exempt organic compounds shall be determined using either ASTM D4457 or SCAQMD Method 303, including updates and revisions.
Section 129.77(u) specifies that the VOC content of a plastic cement welding adhesive or primer shall be determined using SCAQMD Method 316A, including updates and revisions.
Section 129.77(v) specifies that to determine if a diluent is a reactive diluent, the percentage of the reactive organic compound that becomes an integral part of the finished material shall be determined using SCAQMD Method 316A, including updates and revisions.
Section 129.77(w) specifies the procedure for determining the composite vapor pressure of organic compounds in cleaning materials.
Section 129.77(x) specifies that the vapor pressure of each component in the cleaning material subject to § 129.77(w) shall be determined from either ASTM 2879 or one or more of the listed references, including updates and revisions.
Section 129.77(y) specifies that if air pollution control equipment is used to meet the requirements of this section, the owner or operator shall determine the capture efficiency and the control efficiency using certain procedures.
Section 129.77(z) specifies that the active and passive solvent losses from spray gun cleaning systems shall be determined using the SCAQMD Method, General Test Method for Determining Solvent Losses from Spray Gun Cleaning Systems, including updates and revisions.
New § 129.77(aa) allows for use of another test method to determine the VOC or solids content of a product if a request is submitted to the Department in writing, the request demonstrates that the test method provides results that accurately determine the concentration of VOCs in the product or its emissions, and the request is approved by the Department in writing.
Section 129.77(bb) specifies the method for calculating the VOC content of adhesive, sealant, adhesive primer or sealant primer products that do not contain reactive diluents.
Section 129.77(cc) specifies the method for calculating the VOC content for adhesive, sealant, adhesive primer or sealant primer products that contain reactive diluents.
Section 129.77(dd) specifies the method for calculating the VOC content for low-solids adhesive, sealant, adhesive primer or sealant primer products.
Section 129.77(ee) specifies the method for calculating percent VOC by weight.
Section 129.77(ff) specifies how to convert from units of grams per liter to units of pounds per gallon.
Section 129.77, Table V lists the VOC content limits for the regulated adhesives, sealants, adhesive primers and sealant primers, as applied. The VOC content limits for nonporous architectural and porous architectural sealant primers are corrected in the final-form rulemaking, as they had been transposed in the proposed rulemaking.
Section 129.77, Table VI lists the VOC content limits for adhesive or sealant products applied to particular substrates, as applied.
The final-form rulemaking adds Chapter 130, Subchapter D. Many of the revisions to the proposed rulemaking are made for the purpose of clarity. The compliance date is also changed, based on the anticipated publication date of the final-form rulemaking.
Section 130.701 (relating to applicability) in the final-form rulemaking establishes that, except as provided in § 130.703 (relating to exemptions and exceptions), this subchapter applies to a person who, on or after January 1, 2012, sells, supplies, offers for sale, manufactures for sale for use or application in this Commonwealth, or uses or applies for compensation in this Commonwealth one or more of the following products subject to this subchapter: an adhesive, sealant, adhesive primer or sealant primer; an adhesive or sealant product applied to particular substrates; or a surface preparation solvent or cleanup solvent product.
Section 130.702(a) (relating to emission standards) establishes that, except as provided in § 130.703, a person may not sell, supply, offer for sale or manufacture for sale for use or application in this Commonwealth an adhesive, sealant, adhesive primer or sealant primer manufactured on or after January 1, 2012, which contains VOCs in excess of the applicable VOC content limit specified in Table I (relating to VOC content limits for adhesives, sealants, adhesive primers and sealant primers, as applied).
Section 130.702(a) also establishes that, except as provided in § 130.703, a person may not sell, supply, offer for sale or manufacture for sale for use or application in this Commonwealth an adhesive or sealant product manufactured on or after January 1, 2012, applied to particular substrates, which contains VOCs in excess of the applicable VOC content limit in Table II (relating to VOC content limits for adhesive or sealant products applied to particular substrates, as applied).
Section 130.702(b) establishes that, except as provided in § 130.703, a person may not use or apply for compensation within this Commonwealth an adhesive, sealant, adhesive primer or sealant primer manufactured on or after January 1, 2012, which contains VOCs in excess of the applicable VOC content limit specified in Table I, or an adhesive or sealant product manufactured on or after January 1, 2012, applied to a substrate listed in Table II if the product contains VOCs in excess of the applicable VOC content limit in Table II.
Section 130.702(c) describes how the VOC content limits in Table II will apply.
Section 130.702(d) establishes additional requirements for persons using or applying a surface preparation solvent or cleanup solvent.
Section 130.702(e) establishes the methods that must be followed for removing adhesive, sealant, adhesive primer or sealant primer from the parts of spray application equipment.
Section 130.702(f) establishes that a person who uses or applies a product subject to this subchapter shall store or dispose of all absorbent materials, including cloth or paper, which are moistened with adhesives, sealants, primers or solvents subject to this subchapter in nonabsorbent containers at the facility or location of use that are kept closed except when placing materials in or removing materials from the container.
Section 130.702(g) establishes that a person may not solicit, require or specify the use or application of a product subject to this subchapter if the use or application would result in a violation of this subchapter. The final-form rulemaking specifies that the prohibition of subsection (g) applies to all written or oral contracts created on or after January 1, 2012, under which an adhesive, sealant, adhesive primer, sealant primer, surface preparation solvent or cleanup solvent subject to this section is to be used or applied at a location in this Commonwealth.
Section 130.702(h) specifies that a person who, for compensation, uses or applies an adhesive, sealant, adhesive primer or sealant primer in this Commonwealth may not add solvent to the adhesive, sealant, adhesive primer or sealant primer in an amount in excess of the manufacturer's recommendation for application, if this additional solvent causes the product to exceed the applicable VOC content limit listed in Table I or II.
Section 130.702, Table I lists the VOC content limits for the regulated adhesives, sealants, adhesive primers and sealant primers, as applied. The final-form rulemaking contains new VOC content limits in Table I for ceramic tile installation adhesives, single-ply roof membrane sealants and ''other'' sealant primers, as these limits were printed incorrectly in the proposed rulemaking.
Section 130.702, Table II lists the VOC content limits for the regulated adhesive or sealant products applied to particular substrates, as applied.
Section 130.703 provides certain exemptions from Subchapter D. Subsection (a) provides exemptions for products being tested or evaluated in a research and development, quality assurance or analytical laboratory, if records are maintained as required under § 130.704 (relating to recordkeeping requirements); products that are subject to § 129.73 or Chapter 130, Subchapter B or C; adhesives and sealants that contain less than 20 grams of VOC per liter of adhesive or sealant, less water and less exempt compounds, as applied; cyanoacrylate adhesives; adhesives, sealants, adhesive primers or sealant primers that are sold or supplied by the manufacturer or supplier in containers with a net volume of 16 fluid ounces or less or a net weight of 1 pound or less, except plastic cement welding adhesives and contact adhesives; and contact adhesives that are sold or supplied by the manufacturer or supplier in containers with a net volume of 1 gallon or less.
Section 130.703(b) provides exemptions from the requirements of Subchapter D for the use, application, sale, supply, offer for sale or manufacture for sale for use in this Commonwealth of adhesives, sealants, adhesive primers, sealant primers, surface preparation solvents and cleanup solvents in certain operations, including tire repair operations, if the label of the tire repair adhesive states ''For tire repair only;'' the assembly, repair and manufacture of aerospace components or undersea-based weapons systems; the manufacture of medical equipment; and certain plaque laminating operations.
The final-form rulemaking removes proposed § 130.703(c) and (d), which provided a phased-in compliance schedule for the use and application of single-ply roof membrane materials and an exemption for the sale, supply, offer for sale or manufacture for sale of these materials prior to January 1, 2012. The proposed schedule and removes exemption are deleted because the change in compliance date to January 1, 2012, make them unnecessary.
The final-form rulemaking removes proposed § 130.703(e) and (f), which contained ''small quantity'' exemptions similar to those in § 129.77(m) and (n). Proposed subsection (e) provided an exemption from many of the requirements of § 130.702 if the total VOC emissions from all adhesives, sealants, adhesive primers and sealant primers used at a facility were less than 200 pounds or an equivalent volume, per calendar year. Proposed subsection (f) provided an exemption for the use of a noncomplying adhesive, sealant, adhesive primer, sealant primer, surface preparation solvent or cleanup solvent if the total volume of noncomplying products applied facility-wide did not exceed 55 gallons per calendar year. In response to comment, the Board determined that the small quantity exemptions are applicable only for the owner and operator of a facility and these sources are regulated under § 129.77.
Section 130.703(c) in the final-form rulemaking provides an exemption for an adhesive, sealant, adhesive primer or sealant primer product if the manufacturer or distributor keeps records demonstrating that the product is intended for shipment and use outside of this Commonwealth and that the manufacturer or distributor has taken reasonably prudent precautions to assure that the product is not distributed to or within this Commonwealth.
Section 130.703(d) precludes the exercise of the exemption in subsection (c) for an adhesive, sealant, adhesive primer or sealant primer product sold, supplied or offered for sale by a person to a retail outlet in this Commonwealth.
Section 130.703(e) specifies that Subchapter D does not apply to an adhesive, sealant, adhesive primer, sealant primer, surface preparation solvent or clean-up solvent product that is sold or supplied for use or application as part of a manufacturing process at a facility subject to § 129.77.
Section 130.703(f) specifies that Subchapter D does not apply to an adhesive, sealant, adhesive primer, sealant primer, surface preparation solvent or cleanup solvent used or applied at a private residence for a noncommercial purpose or by a person who is not seeking compensation.
Section 130.704 specifies that on and after January 1, 2012, a person who sells, supplies, offers for sale, manufactures for sale for use or application in this Commonwealth, or uses or applies in this Commonwealth an adhesive, sealant, adhesive primer, sealant primer, surface preparation solvent or cleanup solvent product subject to Subchapter D shall maintain records demonstrating compliance with this subchapter, including certain information. This section also specifies that all records made to determine compliance with this section shall be maintained onsite for 5 years from the date the record is created and made available to the Department upon request. This section is amended in the final-form rulemaking in response to comment to specify that records of volume must indicate monthly volume and that records shall be made available to the Department upon receipt of a written request.
Section 130.705(a) (relating to compliance procedures and test methods) specifies, with certain exceptions, that the VOC and solids content of nonaerosol adhesives, including one-part moisture cure urethane adhesives and silicone adhesives, sealants, adhesive primers, sealant primers, surface preparation solvents and cleanup solvents shall be determined using either EPA Reference Method 24 or SCAQMD Method 304, including updates and revisions.
Section 130.705(b) is added in the final-form rulemaking, in response to public comment, to add a test method for determining the volatile matter and solids content of one-part or multiple part reactive adhesives, except one-part moisture cure urethane adhesives and silicone adhesives.
Section 130.705(c) specifies that the identity and concentration of exempt organic compounds shall be determined using either ASTM D4457 or SCAQMD Method 303, including updates and revisions.
Section 130.705(d) specifies that the VOC content of a plastic cement welding adhesive or primer shall be determined using SCAQMD Method 316A, including updates and revisions.
Section 130.705(e) specifies that to determine if a diluent is a reactive diluent, the percentage of the reactive organic compound that becomes an integral part of the finished material shall be determined using SCAQMD Method 316A, including updates and revisions.
Section 130.705(f) specifies the procedure for determining the composite vapor pressure of organic compounds in cleaning materials.
Section 130.705(g) specifies that the vapor pressure of each component in the cleaning material subject to § 130.705(f) shall be determined from either ASTM 2879 or one or more of the listed references, including updates and revisions.
Section 130.705(h) specifies that the active and passive solvent losses from spray gun cleaning systems shall be determined using the SCAQMD Method, General Test Method for Determining Solvent Losses from Spray Gun Cleaning Systems, including updates and revisions.
New § 130.705(i) allows for use of another test method to determine the VOC or solids content of a product if a request is submitted to the Department in writing, the request demonstrates that the test method provides results that accurately determine the concentration of VOCs in the product or its emissions and the request is approved by the Department in writing.
Section 130.705(j) specifies the method for calculating the VOC content of adhesive, sealant, adhesive primer or sealant primer products that do not contain reactive diluents.
Section 130.705(k) specifies the method for calculating the VOC content for adhesive, sealant, adhesive primer or sealant primer products that contain reactive diluents.
Section 130.705(l) specifies the method for calculating the VOC content for low-solids adhesive, sealant, adhesive primer or sealant primer products.
Section 130.705(m) specifies the method for calculating percent VOC by weight.
Section 130.705(n) specifies how to convert from units of grams per liter to units of pounds per gallon.
Section 130.706 (relating to container labeling) specifies that on and after January 1, 2012, each manufacturer of an adhesive, sealant, adhesive primer or sealant primer product subject to this subchapter shall display certain information on the product container or label.
The final-form rulemaking adds §§ 130.707 and 130.708 (relating to product dating; and sell-through of products) to allow the sell-through of noncomplying product manufactured before January 1, 2012, if the product container or package displays the date on which the product was manufactured.
F. Summary of Major Comments and Responses
The Board approved publication of the proposed rulemaking at its meeting of December 16, 2008. The proposed rulemaking was published at 39 Pa.B. 1636 (April 4, 2009). Three hearings were held on May 4, 7 and 8, 2009, in Pittsburgh, Norristown and Harrisburg, respectively. The public comment period closed on June 8, 2009. The Board received public comments from 12 commentators. The Independent Regulatory Review Commission (IRRC) also provided comments.
Definitions
Several commentators expressed concern with the Department's definition of the term ''metal to urethane/rubber molding or casting adhesive.'' They suggested that the use of the word ''heater'' in this definition was a typographical error and should be replaced with the word ''heated.'' The commentators also suggested deleting the phrase ''to fabricate products like rollers for computer printers or other paper handling equipment'' because it could be misinterpreted by regulators to restrict the category only to paper handling products and not to all products that use adhesive to bond metal and urethane/rubber. The Board agrees and amended the definition accordingly.
One commentator recommended that the term and definition of ''metal to urethane/rubber molding or casting adhesive'' be deleted and replaced with a term and definition modeled after a term and definition for ''rubber vulcanization adhesive/primer'' in the (California) San Joaquin Valley Air Quality Management District Rule 4653—Adhesives due to confusion the commentator asserts may result from customers being subject to a number of VOC and hazardous air pollutants (HAPs) emission standards. The Board disagrees and retained the proposed term and definition of ''metal to urethane/rubber molding or casting adhesive,'' amended as previously described, for consistency with the OTC Model Rule and the regulations of other OTR member states.
A commentator suggested that the term ''rubber'' be defined as in the (California) Bay Area Air Quality Rule 8.51 (relating to adhesive and sealant products) to accommodate the concerns of the Polyurethane Manufacturers Association and its members. The Board disagrees with the commentator's recommendation. The Board did not receive comments from the Polyurethane Manufacturers Association concerning the definition of the term ''rubber'' and the definition in the Bay Area Air Quality Management District Rule 8.51 is similar to the definition in the Board's rulemaking. In addition, the definition of the term ''rubber'' in the proposed rulemaking is consistent with the definition in the Control Techniques Guidelines (CTG) for Miscellaneous Industrial Adhesives published by the EPA (EPA-453/R-08-005, September 2008) and with the definition in the OTC Model Rule. The Board retained the proposed definition of the term ''rubber'' for consistency with the OTC Model Rule.
A commentator recommended that the definition of the term ''single-ply roof membrane'' be expanded to include thermoplastic membranes like thermoplastic polyolefin (TPO) and polyvinyl chloride (PVC), as these materials are also considered part of the single-ply roofing market by the commercial roofing industry. The Board agrees with the commentator that the definition of ''single-ply roof membrane'' should be expanded to include TPO and PVC. The definition of this term has been amended in the final-form rulemaking to include TPO, PVC and ketone ethylene ester. This change is consistent with the final-form definition of this term promulgated by Rhode Island and Connecticut. These states are members of the OTR, as is the Commonwealth.
IRRC requested clarification on the Editor's Note for the term ''fiberglass'' and questioned if the Board would have two definitions for the term ''fiberglass.'' The Board replies that it published a definition for the term ''fiberglass'' in § 121.1 in two separate proposed rulemakings. The definition of the term in this proposed rulemaking specified that the definition is for purposes of §§ 129.77 and 130.702. The definition of this term in the rulemaking published for comment at 38 Pa.B. 1831 (April 19, 2008), concerning emissions from glass melting furnaces, specified that that definition is for purposes of §§ 129.301—129.310 (relating to control of NOx emissions from glass melting furnaces). That rulemaking was published as a final at 40 Pa.B. 3328 (June 19, 2010). The definition of the term ''fiberglass'' in this final-form rulemaking for adhesives, sealants, primers and solvents includes both definitions, as specified.
Implementation of Single-ply Roof Membrane Requirements
Several commentators expressed support for the rulemaking on behalf of the ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM) roofing industry. The Board appreciates the commentators' support.
Due to concerns about the effects of cold weather and intense temperature swings and freeze-thaw cycles on the installation of EPDM roofing in this Commonwealth, the EPDM industry requested a transitional period that would allow the EPDM industry adequate time to field test new VOC-compliant adhesive formulations during colder months and to train the approximately 25,000 roofing crew members employed in this Commonwealth in the effective use of VOC-compliant adhesives under colder temperature conditions. Another commentator on behalf of the EPDM industry stated that the industry is committed to having a year-round product commercialized by January 1, 2012. The Board amended the final-form rulemaking to require compliance with the VOC content limits for adhesives, sealants, primers and solvents, including single-ply roofing membrane products, by January 1, 2012. This compliance date will provide EPDM roofing manufacturers and roofing contractors in this Commonwealth adequate time to develop VOC-compliant products and perfect the application practices that will be effective on a year-round basis. This new compliance date removes the need to have a phased-in compliance period for the use and application of single-ply roofing membrane products, which was included in the proposed rulemaking.
Sell-Through and Use-Through Provisions; Date-Coding Provision
Two commentators suggested that there is an inconsistency between proposed § 130.702(a) and (b) in the provisions for the sell-through and use-through of noncomplying products. They noted that § 130.702(a) prohibits the sale, supply, offer for sale or manufacture for sale in this Commonwealth of noncomplying products manufactured on or after the compliance date and that proposed § 130.702(b) prohibited the use or application of noncomplying products in this Commonwealth on or after the compliance date, even if the product was manufactured prior to the compliance date. The commentators recommended that specific language be added indicating that the use and application of noncomplying products manufactured after the compliance date of the rulemaking are prohibited. The Board agrees and amended final-form § 130.702(b) to clarify that noncomplying products manufactured on and after the amended compliance date of January 1, 2012, may not be used or applied for compensation in this Commonwealth. The Board also amended the final-form rulemaking to add §§ 130.707 and 130.708 to allow the sell-through of noncomplying product manufactured before January 1, 2012, if the product container or package displays the date on which the product was manufactured.
A commentator suggested that it would be simpler and more cost effective to make the compliance deadline 24 months from the date that the final-form rulemaking is published than to have a sell-through or use-through provision. The commentator stated a sell-through or use-through provision would force users to stockpile product, which the commentator described as a costly expense in difficult economic times. The Board disagrees. Many complying adhesives, sealants, primers and solvents have already been developed, or reformulated from noncomplying products, due to similar rules having been promulgated in California and other states in the OTR. The final-form rulemaking has been amended to include date-coding and sell-through provisions to allow for the sell-through of noncomplying product manufactured before the compliance date.
Burden of Compliance
A commentator suggested that the proposed amendments place the burden of compliance on the manufacturer and seller of adhesives, sealants, primers or solvents in two ways: to ensure that noncompliant product is not sold to customers that do not have control systems in place, and for technical service and regulatory support costs to assist its customers in identifying and requalifying alternate adhesive systems or determining if their use meets the allowable exemptions. The commentator recommended that the language that places a compliance burden on the manufacturer and seller be removed from the proposed rulemaking. The commentator also asked how the requirement not to sell noncompliant product to customers that do not have control systems in place will be enforced equally between manufacturers of adhesives located in this Commonwealth and those located outside the United States. The Board disagrees with the commentator's characterization of the rulemaking. An adhesive, sealant, adhesive primer, sealant primer, surface preparation solvent or cleanup solvent product intended for use or application at a manufacturing facility subject to § 129.77 does not require the manufacturer or supplier of the product to verify that the facility has a control system in place. Under § 130.703(e) (proposed § 130.703(i)), Subchapter D does not apply to a product sold or supplied for use or application as part of a manufacturing process at a facility subject to § 129.77. The burden of compliance will fall on the owner or operator of the manufacturing facility that is using or applying noncomplying product to demonstrate that the noncomplying product was used or applied in accordance with § 129.77(g), which lists the requirements for the use of add-on air pollution control equipment to control emissions of VOC from noncomplying product subject to § 129.77.
Three commentators expressed concern with the compliance date of the proposed regulation and stated that the Department must provide a reasonable compliance date that allows for implementation of the rule's requirements. IRRC commented that because the Board did not know exactly when this final-form rulemaking would officially be promulgated, the Board should consider replacing the April 15, 2010, compliance date with a reference to a specific amount of time after the effective date of the final-form rulemaking. The Board agrees that it must provide a reasonable compliance date. The proposed compliance date of April 15, 2010, has been amended to January 1, 2012, in the final-form rulemaking. The Board does not agree that it must replace the proposed compliance date with a reference to a specific amount of time after the effective date of the final-form rulemaking. The Board is able to estimate within a reasonable time frame when this final-form rulemaking will be published and effective and extended the compliance date taking that time frame and the needs of the regulated industry into account.
The same three commentators suggested that the proposed compliance deadline is not achievable to design, build, install, test and obtain permit approval of add-on air pollution control devices. Two of these commentators also asserted that it is not realistic to develop, reformulate, test and achieve final customer approval for a new adhesive in less than 1 year. The commentators suggested that the rulemaking allow 2 years after adoption of the final-form rulemaking for the regulated industry to make the appropriate changes to their operations and to allow for proper reformulation and customer acceptance testing of adhesives. The Board disagrees that the regulated industry needs 2 years after adoption of the final-form rulemaking to comply with the VOC content requirements. The Board agrees, however, that the January 1, 2012, compliance deadline in the final-form rulemaking might not be achievable for the design and installation of add-on controls. The Board amended proposed § 129.77(g) to provide the option for an extension to the compliance date for the owner or operator of a facility that intends to comply with this section through the use of add-on air pollution control equipment.
A commentator expressed concern that its products manufactured in this Commonwealth will be at a competitive disadvantage in the marketplace due to inadequate time for proper reformulation and customer acceptance testing. The Board disagrees that the commentator will be at a competitive disadvantage. The Board amended the final-form rulemaking to require compliance beginning January 1, 2012. Further, many states, including California and several members of the OTR, have implemented rules with VOC content limits and requirements similar to the Board's proposed rulemaking. Manufacturers and users in states outside this Commonwealth will be required to manufacture and buy products that meet the same limits as were in the proposed rulemaking, creating a market for complying products manufactured in this Commonwealth. Additionally, the EPA issued the CTG for Miscellaneous Industrial Adhesives in 2008. The CTG provides states in ozone nonattainment areas and in the OTR with guidance on what constitutes RACT for emissions of VOCs from miscellaneous industrial adhesives. The EPA reviewed the California rules and the OTC Model Rule for Adhesives and Sealants prior to developing its guidance for RACT for miscellaneous industrial adhesives. The OTR states are required to adopt RACT regulations for miscellaneous industrial adhesives, based on the EPA's CTG.
The same commentator expressed concern that its customers outside of this Commonwealth would incur additional costs associated with reformulation. The Board disagrees. Noncomplying products may be sold outside of this Commonwealth to a customer in a state or region that does not have the VOC content limits that are proposed to be implemented in this Commonwealth.
The commentator suggested that the rule imposes a competitive disadvantage on manufacturers in this Commonwealth. Manufacturers outside of this Commonwealth are able to choose adhesives on the basis of performance and cost without incurring additional operational costs to control emissions beyond what is required by the EPA. The Board disagrees that the proposed rulemaking would impose a competitive disadvantage on manufacturers in this Commonwealth. Noncomplying products may be sold outside of this Commonwealth to a customer in a state or region that does not have the VOC content limits implemented in this Commonwealth. Many states, including California and several members of the OTR, have implemented rules with VOC content limits and requirements similar to those in the Board's final-form rulemaking. Manufacturers and users in these states will be required to buy products that meet the same limits as those in the final-form rulemaking, creating a market for complying products manufactured in this Commonwealth.
The commentator stated that compliance with the Plastic and Metal Surface Coating National Emissions Standards for Hazardous Air Pollutants (NESHAP) is based on a 12-month rolling average with an adhesive coating category limit expressed in pounds of HAP per gallon of applied solids rather than pounds per gallon or grams per liter. This allows facilities to use noncomplying products as long as the overages are compensated by other materials that are significantly below the limit. The commentator recommended that the Department consider using a rolling average in the proposed rule. The Board disagrees with the commentator's suggestion to adopt a 12-month rolling average. Compliance with the requirements of this proposed rulemaking is expected to be through the use of compliant products, consistent with the requirements of the OTC Model Rule. An owner or operator of a facility may seek compliance through the use of add-on controls to control the emissions from noncomplying products. Compliance using add-on controls will be evaluated on a daily basis, consistent with the OTC Model Rule. An owner or operator of a facility may also seek compliance with § 129.77 through the use of an equivalency under § 129.51(a). This option would allow the owner or operator to request approval of an averaging approach specified in a plan approval application and memorialized in a permit under the equivalency provision.
VOC Test Methodology
The commentator requested that an EPA-approved alternative test method for two-component reactive adhesives, codified in Appendix A of the Plastic Surface Coating NESHAP (40 CFR Part 63, Subpart PPPP, Appendix A (relating to determination of weight volatile matter content and weight solids content of reactive adhesives)), be added to §§ 129.77(s) and 130.705(a). The Board reviewed the EPA Reference Method, Determination of Weight Volatile Matter Content and Weight Solids Content of Reactive Adhesives, for two-component reactive adhesives codified in 40 CFR Part 63, Subpart PPPP, Appendix A and agrees that it should be included on the list of test methods listed in §§ 129.77(s) and 130.705(a). This revision has been made to the final-form rulemaking.
Written and Oral Contracts
IRRC noted that proposed §§ 129.77(i) and 130.702(g) included a prohibition on the use of a material that would result in a violation of the regulation and that this prohibition applies to ''all written or oral contracts'' under which any of these materials would be used. IRRC asked if the Board intends to apply this provision retroactively. If so, IRRC requested that the Board outline its authority to do so. If not, IRRC requested that the Board clarify the provisions to state that they will be applied prospectively. The Board appreciates IRRC's concern and amended the final-form rulemaking to clarify that this prohibition applies to written or oral contracts that are created on or after the compliance date of this final-form rulemaking.
Records and Reporting Requirements
IRRC requested clarification on how the records required under proposed §§ 129.77(l)(4), (n) and (o), and 130.703(b)(4), (e) and (f) shall be recorded and maintained by the owner or operator. The Board disagrees that the rulemaking should be amended for clarity on recordkeeping. Proposed § 129.77(l)(4), (n) and (o) (final-form subsections (l), (m) and (n)) states that an owner or operator claiming an exemption under the section shall record and maintain operational records sufficient to demonstrate compliance with this exemption, in accordance with proposed subsections (p)—(r) (final-form subsections (o)—(q)). Section 130.703(b)(4) states that a person claiming an exemption under this paragraph shall record and maintain operational records sufficient to demonstrate compliance with this exemption, in accordance with § 130.704. Proposed § 130.703(e) and (f) have been deleted from the final-form rulemaking, mooting the comment with regard to these two subsections. Requiring the owners and operators of regulated facilities to maintain records is a standard requirement. This requirement is found in many Board-approved regulations, including § 129.52(g) (relating to surface coating processes), for instance, and the owners and operators of regulated sources have not had difficulty understanding or complying with requirements.
IRRC requested clarification of the requirement in proposed § 129.77(r)(1) for maintaining records. IRRC asked whether the records can be maintained in electronic or paper format and stated that the final-form rulemaking should indicate in what format these records must be maintained. The Board disagrees that the final-form rulemaking must specify in what format the records must be maintained. Requiring the owners and operators of regulated facilities to maintain records is a standard requirement found in many Board-approved regulations, including § 129.52(g), for instance. The owners and operators of regulated sources have not had difficulty understanding or complying with this requirement.
IRRC requested clarification of whether the Department's requests for records under proposed § 129.77(r)(2) will be made orally or in writing and stated that the final-form rulemaking should indicate in what format the requests will be made. The Board agrees and amended the final-form rulemaking to specify that the records shall be submitted to the Department upon receipt of a written request.
G. Benefits, Costs and Compliance
Benefits
The citizens of this Commonwealth will be the major benefactors from this final-form rulemaking through reduced exposure to a variety of solvents, including HAPs, that are used in a variety of adhesive, sealant, adhesive primer and sealant primer products. This final-form rulemaking will result in improved air quality by reducing VOC ozone precursor emissions from the industrial and commercial use and application of the regulated adhesive, sealant and primer products. Benefits will also occur from reduced VOC content in surface preparation solvent and cleanup solvent products. The final-form rulemaking will encourage the implementation of new technologies and practices, which will reduce emissions of VOCs and HAPs throughout this Commonwealth.
Implementation of the VOC content limits for adhesive, sealant, primer and solvent products included in the final-form rulemaking is anticipated to provide additional VOC emission reductions of 21.8 tons per summer day (tpsd) beginning with the 2012 ozone monitoring season. Ozone monitoring season (April 1 through October 31) VOC emission reductions from this final-form rulemaking would be approximately 4,665.2 tons (21.8 tpsd × 214 ozone monitoring season days). Assuming that there are approximately 12 million people living in this Commonwealth, the average ozone monitoring season VOC emissions reduction is calculated to be 0.78 pound of VOC emissions reduced per resident. Annual VOC emission reductions from this final-form rulemaking would be approximately 7,957 tons (21.8 tpsd × 365 days per year) or 1.3 pounds of VOC emissions reduced per resident per year.
Compliance Costs
The cost of complying with the new requirements includes the cost of using or developing alternative product formulations, including product formulations for low VOC-content or water-based adhesive, sealant, adhesive primer, sealant primer, surface preparation solvent and cleanup solvent products. Based on information provided by the Ventura County Air Pollution Control District (VCAPCD), the CARB determined that the cost-effectiveness of the VCAPCD adhesives rule, which formed the basis of the CARB 1998 RACT/BARCT Determination upon which the OTC 2006 Model Rule is based, ranges from a savings of $1,060 per ton to a cost of $2,320 per ton of VOC reduced. Any costs are likely to be less in the OTR, because some of the research and reformulation costs incurred for products sold in California will not have to be incurred again for products sold in the OTR. The CARB also reports a cost-effectiveness of $9,000 to $110,000 per ton of VOC reduced should the use of add-on control equipment to comply with the requirements be necessary.
The Department anticipates similar costs in this Commonwealth. MACTEC Federal Programs, a consultant to the OTC, indicated in its report, ''Identification and Evaluation of Candidate Control Measures, Final Technical Support Document,'' that the OTC Adhesives, Sealants and Primers Model Rule would reduce emissions of VOC by approximately 21.8 tpsd in this Commonwealth. Ozone monitoring season (April 1 through October 31) VOC emission reductions from this final-form rulemaking would be approximately 4,665.2 tons (21.8 tpsd × 214 ozone monitoring season days). Assuming that there are approximately 12 million people living in this Commonwealth, the average ozone season VOC emissions reduction is calculated to be 0.78 pound of VOC emissions reduced per resident of this Commonwealth.
The total ozone monitoring season costs are calculated by multiplying the maximum estimated cost of $2,320 per ton of VOC emissions reduced times 4,665.2 tons per ozone monitoring season, which equals approximately $10,823,264 per ozone monitoring season. The maximum ozone monitoring season cost per resident of this Commonwealth will be approximately 90¢.
Annual VOC emission reductions from this final-form rulemaking will be approximately 7,957 tons (21.8 tpsd × 365 days per year) or 1.3 pounds of VOC emissions reduced per resident of this Commonwealth per year. Annual costs will be $2,320 per ton of VOC emissions reduced times 7,957 tons per year or $18,460,000. The maximum annual cost per resident of this Commonwealth will be approximately $1.55.
Cost savings will be incurred if reformulated products are less expensive, with the possibility that residents of this Commonwealth could realize savings of 41¢ per ozone season per resident ($1,060 × 4,665.2 tons divided by 12,000,000 residents) or 70¢ annually per resident ($1,060 × 7,957 tons divided by 12,000,000 residents).
Owners or operators of facilities or stationary sources using regulated adhesive, sealer, primer and solvent products could incur costs of $9,000 to $110,000 per ton of VOC emissions reduced, should the use of add-on control equipment be necessary to comply with the requirements of this final-form rulemaking, based on CARB estimates. However, fewer than 20 facilities in this Commonwealth are expected to be subject to the applicability of this rulemaking. Approximately 16 of these affected facilities have permits that establish requirements for the use of products that are regulated under this rulemaking.
Compliance Assistance Plan
The Department plans to educate and assist the public and regulated community in understanding the new requirements and how to comply with them. This will be accomplished through the Department's ongoing compliance assistance program.
Paperwork Requirements
The final-form rulemaking includes recordkeeping and reporting requirements in § 129.77 for affected owners and operators of facilities that use or apply the regulated adhesive, sealant, adhesive primer, sealant primer, surface preparation solvent and cleanup solvent products. These recordkeeping requirements include keeping lists of each regulated product in use or in storage; a data sheet or material list for each product that provides the name of the product, manufacturer's identification and use for the product; the VOC content for the product as supplied; the catalysts, reducers or other components used and the mix ratio; the VOC content or vapor pressure of each product as applied, if solvent or other VOC is added to the product before application; the volume purchased or produced of each product; and the monthly volume of each product used or applied as part of a manufacturing process at the facility of each product.
If the owner or operator of a facility chooses to use an add-on air pollution control device to comply with § 129.77, the final-form rulemaking requires recording and maintaining daily records of certain information.
For an adhesive, sealant, adhesive primer and sealant primer product subject to the laboratory testing exemption, the person conducting the testing shall make and maintain records of all products used, including the following information: the product name; the product category of the material or type of application; and the VOC content of the material.
Records made to determine compliance with § 129.77 shall be maintained onsite for 5 years from the date the record is created and made available to the Department upon receipt of a written request.
The final-form rulemaking includes recordkeeping and reporting requirements in Chapter 130, Subchapter D for a person who sells, supplies, offers for sale or manufactures for sale for use in this Commonwealth an adhesive, sealant, adhesive primer, sealant primer, surface preparation solvent or cleanup solvent product subject to this subchapter. The person shall maintain records demonstrating compliance with this subchapter, including the following information: a data sheet or material list which provides the material name, manufacturer identification and material application for each product; the VOC content of each product, as supplied; and the number of gallons of product sold in this Commonwealth.
A person who uses or applies an adhesive, sealant, adhesive primer, sealant primer, surface preparation solvent or cleanup solvent product subject to Chapter 130, Subchapter D shall maintain records demonstrating compliance with this subchapter, including the following information: a list of each adhesive, sealant, adhesive primer, sealant primer, surface preparation solvent and cleanup solvent product in use and in storage; a data sheet or material list which provides the product name, manufacturer identification and use or material application for each product included on the list; the VOC content of each product on the list, as supplied; catalysts, reducers or other components used and the mix ratio; the VOC content or vapor pressure of each product on the list, as applied, if solvent or other VOC is added to the product before application; and the monthly volume used of each product on the list.
For an adhesive, sealant, adhesive primer and sealant primer product subject to the laboratory testing exemption in § 130.703(a)(1), the person conducting the testing shall make and maintain records of all materials used, including the following information: the product name; the product category of the material or type of application; and the VOC content of the material.
Records made to determine compliance with Chapter 130, Subchapter D shall be maintained for 5 years from the date the record is created and made available to the Department upon receipt of a written request.
H. Pollution Prevention
The Pollution Prevention Act of 1990 (42 U.S.C.A. §§ 13101—13109) established a National policy that promotes pollution prevention as the preferred means for achieving state environmental protection goals. The Department encourages pollution prevention, which is the reduction or elimination of pollution at its source, through the substitution of environmentally friendly materials, more efficient use of raw materials and the incorporation of energy efficiency strategies. Pollution prevention practices can provide greater environmental protection with greater efficiency because they can result in significant cost savings to the owners and operators of facilities that permanently achieve or move beyond compliance. This final-form rulemaking incorporates the following pollution prevention incentives:
The final-form rulemaking will assure that the citizens and the environment of this Commonwealth experience the benefits of reduced emissions of VOCs and HAPs from the industrial and commercial use or application of low VOC-content adhesive, sealant, adhesive primer, sealant primer, surface preparation solvent and cleanup solvent products. Although the final-form rulemaking is designed to address ground-level ozone air quality by reducing emissions of ozone precursors, the reformulation of products to meet the VOC content limits will also result in the reduction of HAP emissions, which are also a serious health threat. The final-form rulemaking will result in improved indoor and outdoor air quality for all citizens of this Commonwealth by reducing VOC ozone precursor emissions and HAP compounds. The reduced levels of HAPs will also benefit water quality through reduced loading on water treatment plants and in reduced quantities of HAP compounds in spillage on the ground. Owners and operators of affected facilities may also reduce VOC emissions through the use of add-on controls.
I. Sunset Review
These regulations will be reviewed in accordance with the sunset review schedule published by the Department to determine whether the regulations effectively fulfill the goals for which they were intended.
J. Regulatory Review
Under section 5(a) of the Regulatory Review Act (71 P. S. § 745.5(a)), on March 20, 2009, the Department submitted a copy of the notice of proposed rulemaking, published at 39 Pa.B. 1636, to IRRC and the Chairpersons of the House and Senate Environmental Resources and Energy Committees for review and comment.
Under section 5(c) of the Regulatory Review Act, IRRC and the House and Senate Committees were provided with copies of the comments received during the public comment period, as well as other documents when requested. In preparing the final-form rulemaking, the Department has considered all comments from IRRC, the House and Senate Committees and the public.
Under section 5.1(j.2) of the Regulatory Review Act (71 P. S. § 745.5a(j.2)), on November 3, 2010, the final-form rulemaking was deemed approved by the House and Senate Committees. Under section 5.1(e) of the Regulatory Review Act, IRRC met on November 4, 2010, and approved the final-form rulemaking.
K. Findings
The Board finds that:
(1) Public notice of proposed rulemaking was given under sections 201 and 202 of the act of July 31, 1968 (P. L. 769, No. 240) (45 P. S. §§ 1201 and 1202) and regulations promulgated thereunder. 1 Pa. Code §§ 7.1 and 7.2.
(2) At least a 60-day public comment period was provided as required by law and all comments were considered.
(3) These regulations do not enlarge the purpose of the proposed rulemaking published at 39 Pa.B. 1636.
(4) These regulations are necessary and appropriate for administration and enforcement of the authorizing acts identified in Section C of this preamble.
(5) These regulations are necessary to attain and maintain the ozone NAAQS.
L. Order
The Board, acting under the authorizing statutes, orders that:
(a) The regulations of the Department, 25 Pa. Code Chapters 121, 129 and 130, are amended by amending §§ 121.1 and 129.51 and adding §§ 129.77 and 130.701—130.708 to read as set forth in Annex A, with ellipses referring to the existing text of the regulations.
(Editor's Note: The amendment of § 129.51 and the addition of §§ 130.707 and 130.708 were not included in the proposed rulemaking at 39 Pa.B. 1636.)
(b) The Chairperson of the Board shall submit this order and Annex A to the Office of General Counsel and the Office of Attorney General for review and approval as to legality and form, as required by law.
(c) The Chairperson of the Board shall submit this order and Annex A to IRRC and the Committees as required by the Regulatory Review Act.
(d) The Chairperson of the Board shall certify this order and Annex A and deposit them with the Legislative Reference Bureau as required by law.
(e) This final-form rulemaking will be submitted to the EPA as an amendment to the Pennsylvania SIP.
(f) This order shall take effect immediately upon publication in the Pennsylvania Bulletin.
JOHN HANGER,
Chairperson(Editor's Note: For the text of the order of the Independent Regulatory Review Commission relating to this document, see 40 Pa.B. 6752 (November 20, 2010).)
Fiscal Note: Fiscal Note 7-428 remains valid for the final adoption of the subject regulations.
Annex A
TITLE 25. ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION
PART I. DEPARTMENT OF ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION
Subpart C. PROTECTION OF NATURAL RESOURCES
ARTICLE III. AIR RESOURCES
CHAPTER 121. GENERAL PROVISIONS § 121.1. Definitions.
The definitions in section 3 of the act (35 P. S. § 4003) apply to this article. In addition, the following words and terms, when used in this article, have the following meanings, unless the context clearly indicates otherwise:
ABS welding adhesive or acrylonitrile-butadiene-styrene welding adhesive—An adhesive intended by the manufacturer to weld acrylonitrile-butadiene-styrene (ABS) pipe, which is made by reacting monomers of acrylo- nitrile, butadiene and styrene.
* * * * * Adhesive—
(i) A chemical substance that is applied for the purpose of bonding two surfaces together other than by mechanical means.
(ii) The term does not include coatings or finishing materials.
* * * * * Adhesive primer—
(i) A product intended by the manufacturer for application to a substrate, prior to the application of an adhesive, to provide a bonding surface.
(ii) For purposes of § 129.73 (relating to aerospace manufacturing and rework), a coating applied to an aerospace vehicle or component that does one of the following:
(A) Inhibits corrosion and serves as a primer when applied to bare metal or other surfaces prior to adhesive application.
(B) Is applied to surfaces that can be expected to contain fuel, with the exception of fuel tanks.
Aerosol adhesive—An adhesive packaged as an aerosol product in which the spray mechanism is permanently housed in a nonrefillable can designed for handheld application without the need for ancillary hoses or spray equipment.
* * * * * Aerospace vehicle or component—
(i) For purposes of § 129.73, a fabricated part, processed part, assembly of parts or completed unit, with the exception of electronic components, of an aircraft including airplanes, helicopters, missiles, rockets and space vehicles.
(ii) For purposes of § 129.77 (relating to control of emissions from the use or application of adhesives, sealants, primers and solvents) and Chapter 130, Subchapter D (relating to adhesives, sealants, primers and solvents), the fabricated part, assembly of parts or completed unit of an aircraft, helicopter, missile or space vehicle, including passenger safety equipment.
* * * * * Architectural sealant or primer—
(i) A sealant or sealant primer intended by the manufacturer to be applied to stationary architectural structures, including mobile homes, and their appurtenances.
(ii) Appurtenances to a stationary architectural structure include hand railings, cabinets, bathroom and kitchen fixtures, fences, rain gutters and downspouts, and windows.
As applied—
(i) The VOC and solids content of a coating, adhesive, sealant, adhesive primer, sealant primer, surface preparation solvent or cleanup solvent that is actually used to coat the substrate.
(ii) The term includes the contribution of materials used for in-house dilution of the coating.
As supplied—The VOC and solids content of a coating, adhesive, sealant, adhesive primer, sealant primer, surface preparation solvent or cleanup solvent as sold and delivered to the end user.
* * * * * Automotive glass adhesive primer—An adhesive primer labeled by the manufacturer to be applied to automotive glass prior to installation of the glass using an adhesive or sealant. This primer improves the adhesion to pinch weld and blocks ultraviolet light.
* * * * * CPVC—Chlorinated polyvinyl chloride
CPVC plastic or chlorinated polyvinyl chloride plastic—A polymer of the vinyl chloride monomer that contains 67% chlorine and is normally identified with a CPVC marking.
CPVC welding adhesive or chlorinated polyvinyl chloride welding adhesive—An adhesive labeled for welding of CPVC plastic.
* * * * * Ceramic tile installation adhesive—An adhesive intended by the manufacturer for use in the installation of ceramic tiles.
* * * * * Cleanup solvent—A VOC-containing material used for either of the following:
(i) To remove a loosely held, uncured (that is, not dry to the touch) adhesive or sealant from a substrate.
(ii) To clean equipment used in applying a material.
* * * * * Computer diskette jacket manufacturing adhesive—An adhesive intended by the manufacturer to glue the fold-over flaps to the body of a vinyl computer diskette jacket.
* * * * * Contact bond adhesive—
(i) An adhesive that meets all of the following:
(A) Is designed for application to both surfaces to be bonded together.
(B) Is allowed to dry before the two surfaces are placed in contact with each other.
(C) Forms an immediate bond that is impossible, or difficult, to reposition after both adhesive-coated surfaces are placed in contact with each other.
(D) Does not need sustained pressure or clamping of surfaces after the adhesive-coated surfaces have been brought together using sufficient momentary pressure to establish full contact between both surfaces.
(ii) The term does not include the following:
(A) Rubber cements that are primarily intended for use on paper substrates.
(B) Vulcanizing fluids that are designed and labeled for tire repair only.
* * * * * Cove base—A flooring trim unit, generally made of vinyl or rubber, having a concave radius on one edge and a convex radius on the opposite edge that is used in forming a junction between the bottom wall course and the floor or to form an inside corner.
Cove base installation adhesive—An adhesive intended by the manufacturer to be used for the installation of cove base or wall base on a wall or vertical surface at floor level.
* * * * * Cyanoacrylate adhesive—
(i) For purposes of § 129.77 and Chapter 130, Subchapter D, an adhesive with a cyanoacrylate content of at least 95% by weight.
(ii) A fast-setting, single component adhesive that cures at room temperature.
(iii) The term is also known as ''super glue.''
* * * * * Diluent—A diluting agent added to decrease the viscosity of a material.
* * * * * Drywall installation—The installation of gypsum drywall to studs or solid surfaces using an adhesive formulated for that purpose.
* * * * * Exempt compound or exempt solvent—Specified organic compounds that have been designated by the Administrator of the EPA as having negligible photochemical reactivity and are listed in 40 CFR 51.100 (relating to requirements for preparation, adoption and submittal of implementation plans).
* * * * * Fiberglass—
(i) For purposes of §§ 129.301—129.310 (relating to control of NOx emissions from glass melting furnaces), material consisting of fine filaments of glass that are combined into yarn and woven or spun into fabrics, or that are used as reinforcement in other materials or in masses as thermal or as acoustical insulating product.
(ii) For purposes of §§ 129.77 and 130.702 (relating to emission standards), a material consisting of extremely fine glass fibers.
* * * * * Flexible vinyl—Nonrigid PVC plastic with at least 5% by weight plasticizer content.
* * * * * Indoor floor covering installation adhesive—
(i) An adhesive intended by the manufacturer for use in the installation of wood flooring, carpet, resilient tile, vinyl tile, vinyl backed carpet, resilient sheet and roll or artificial grass.
(ii) The term does not include adhesives used to install ceramic tile or perimeter bonded sheet flooring with vinyl backing onto a nonporous substrate like flexible vinyl.
* * * * * Laminate—A product made by bonding together two or more layers of material.
* * * * * Low-solids adhesive, sealant or primer—An adhesive, sealant, adhesive primer or sealant primer product that contains 120 grams or less of solids per liter of material.
* * * * * Marine deck sealant or marine deck sealant primer—A sealant or sealant primer labeled for application to wooden marine decks.
* * * * * Medical equipment manufacturing—The manufacture of medical devices including catheters, heart valves, blood cardioplegia machines, tracheostomy tubes, blood oxygenators and cardiatory reservoirs.
* * * * * Metal to urethane/rubber molding or casting adhesive—An adhesive intended by the manufacturer to bond metal to high density or elastomeric urethane or molded rubber materials in a heated molding or casting process.
* * * * * Multipurpose construction adhesive—An adhesive intended by the manufacturer for use in the installation or repair of various construction materials, including drywall, subfloor, panel, fiberglass reinforced plastic (FRP), ceiling tile and acoustical tile.
* * * * * Nonmembrane roof installation/repair adhesive—
(i) An adhesive intended by the manufacturer for use in the installation or repair of nonmembrane roofs and that is not intended for the installation of prefabricated single-ply flexible roofing membrane.
(ii) The term includes:
(A) Plastic or asphalt roof cement.
(B) Asphalt roof coating.
(C) Cold application cement.
* * * * * Outdoor floor covering installation adhesive—An adhesive intended by the manufacturer for use in the installation of floor covering that is both of the following:
(i) Not in an enclosure.
(ii) Exposed to ambient weather conditions during normal use.
* * * * * PVC—Polyvinyl chloride.
PVC plastic or polyvinyl chloride plastic—A polymer of the chlorinated vinyl monomer that contains 57% chlorine.
PVC welding adhesive or polyvinyl chloride welding adhesive—An adhesive intended by the manufacturer for use in the welding of PVC plastic pipe.
* * * * * Panel installation—The installation of plywood, predecorated hardboard or tileboard, fiberglass reinforced plastic and similar predecorated or nondecorated panels to studs or solid surfaces using an adhesive formulated for that purpose.
* * * * * Perimeter bonded sheet flooring installation—The installation of sheet flooring with vinyl backing onto a nonporous substrate using an adhesive designed to be applied only to a strip of up to 4 inches wide around the perimeter of the sheet flooring.
* * * * * Plastic cement welding adhesive—
(i) An adhesive intended by the manufacturer for use to dissolve the surface of plastic to form a bond between mating surfaces.
(ii) The term does not include the following welding adhesives:
(A) ABS.
(B) CPVC.
(C) PVC.
Plastic cement welding adhesive primer—A primer intended by the manufacturer for use to prepare plastic substrates prior to bonding or welding.
Plastic foam—Foam constructed of plastics.
Plasticizer—A material, like a high boiling point organic solvent, that is incorporated into a vinyl to increase its flexibility, workability or distensibility, as determined by ASTM Method E-260, including updates and revisions.
Plastics—Synthetic materials chemically formed by the polymerization of organic (carbon-based) substances. Plastics are usually compounded with modifiers, extenders or reinforcers and are capable of being molded, extruded, cast into various shapes and films or drawn into filaments.
* * * * * Porous material—A substance that has tiny openings, often microscopic, into or from which fluids may be absorbed or discharged, including wood, paper and corrugated paperboard.
* * * * * Propellant—A fluid under pressure that expels the contents of a container when a valve is opened.
* * * * * Reactive diluent—A liquid reactive organic compound in an uncured adhesive, sealant or primer that reacts chemically or physically during the curing process to become an integral part of a finished material.
* * * * * Roadway sealant—A sealant intended by the manufacturer for application to public streets, highways and other surfaces, including curbs, berms, driveways and parking lots.
* * * * * Rubber—A natural or manmade rubber substrate, including styrene-butadiene rubber, polychloroprene (neoprene) rubber, butyl rubber, nitrile rubber, chlorosulf- onated polyethylene rubber and ethylene propylene diene terpolymer rubber.
* * * * * SCAQMD—South Coast Air Quality Management District—The California regional government agency responsible for air pollution control in Los Angeles and Orange counties and parts of Riverside and San Bernardino counties.
* * * * * Sealant—
(i) For purposes of § 129.73:
(A) A material used to prevent the intrusion of water, fuel, air or other liquids or solids from certain areas of aerospace vehicles or components.
(B) There are two categories of sealants:
(I) Extrudable/rollable/brushable sealants.
(II) Sprayable sealants.
(ii) For purposes of § 129.77 and Chapter 130, Sub- chapter D:
(A) A material with adhesive properties that is formulated primarily to fill, seal, waterproof or weatherproof gaps or joints between two surfaces.
(B) The term includes caulks.
Sealant primer—A product intended by the manufacturer for application to a substrate, prior to the application of a sealant, to enhance the bonding surface.
* * * * * Sheet rubber installation—
(i) The process of applying sheet rubber liners by hand to metal or plastic substrates to protect the underlying substrate from corrosion or abrasion.
(ii) The term includes laminating sheet rubber to fabric by hand.
* * * * * Single-ply roof membrane—A prefabricated single sheet of rubber or compounded synthetic material, including ethylene propylene diene terpolymer (EPDM), PVC, thermoplastic polyolefin (TPO) or ketone ethylene ester (KEE), that is field applied to a building roof using one layer of membrane material.
Single-ply roof membrane adhesive primer—A primer labeled for use to clean and promote adhesion of the single-ply roof membrane seams or splices prior to bonding.
Single-ply roof membrane installation and repair adhesive—An adhesive labeled for use in the installation or repair of single-ply roof membrane. For purposes of this definition:
(i) Installation includes, as a minimum, attaching the edge of the membrane to the edge of the roof and applying flashings to vents, pipes and ducts that protrude through the membrane.
(ii) Repair includes gluing the edges of torn membrane together, attaching a patch over a hole and reapplying flashings to vents, pipes or ducts installed through the membrane.
Single-ply roof membrane sealant—A sealant labeled for application to single-ply roof membrane.
* * * * * Solvent—Organic compounds which are liquid at standard conditions and which are used as diluents, thinners, dissolvers, viscosity reducers, cleaning agents or other related uses.
* * * * * Structural glazing adhesive—An adhesive intended by the manufacturer to apply glass, ceramic, metal, stone or composite panels to exterior building frames.
* * * * * Subfloor installation—The installation of subflooring material over floor joists, including the construction of load bearing joists. Subflooring material is covered by a finish surface material.
* * * * * Surface preparation solvent—A solvent used to remove dirt, oil and other contaminants from a substrate prior to the application of an adhesive, sealant, adhesive primer or sealant primer.
* * * * * Thin metal laminating adhesive—An adhesive intended by the manufacturer for use in bonding multiple layers of metal to metal or metal to plastic in the production of electronic or magnetic components in which the thickness of the bond line is less than 0.25 mils.
* * * * * Tire repair—A process that includes both of the following steps:
(i) Expanding a hole, tear, fissure or blemish in a tire casing by grinding or gouging.
(ii) Applying adhesive and filling the expanded hole, tear, fissure or blemish with rubber.
Tire tread adhesive—An adhesive intended by the manufacturer for one or more of the following applications:
(i) To the back of precure tread rubber and to the casing and cushion rubber.
(ii) To seal buffed tire casings to prevent oxidation while the tire is being prepared for a new tread.
* * * * * Traffic marking tape—Preformed reflective film intended by the manufacturer for application to public streets, highways and other surfaces, including curbs, berms, driveways and parking lots.
Traffic marking tape adhesive primer—A primer intended by the manufacturer for application to surfaces prior to installation of traffic marking tape.
* * * * * Undersea-based weapons systems components—The fabrication of parts, parts assembly or completed units of a portion of a missile launching system used on undersea ships.
* * * * * Waterproof resorcinol glue—A two-part resorcinol-resin-based adhesive designed for applications where the bond line must be resistant to conditions of continuous immersion in fresh or salt water.
* * * * *
CHAPTER 129. STANDARDS FOR SOURCES
SOURCES OF VOCs § 129.51. General.
(a) Equivalency. Compliance with §§ 129.52, 129.54—129.73 and 129.77 may be achieved by alternative methods if the following exist:
(1) The alternative method is approved by the Department in an applicable plan approval or operating permit, or both.
(2) The resulting emissions are equal to or less than the emissions that would have been discharged by complying with the applicable emission limitation.
(3) Compliance by a method other than the use of a low VOC coating, adhesive, sealant, adhesive primer, sealant primer, surface preparation solvent or cleanup solvent or ink which meets the applicable emission limitation in §§ 129.52, 129.67, 129.73 and 129.77 shall be determined on the basis of equal volumes of solids.
(4) Capture efficiency testing and emissions testing are conducted in accordance with methods approved by the EPA.
(5) Adequate records are maintained to ensure enforceability.
(6) The alternative compliance method is incorporated into a plan approval or operating permit, or both, reviewed by the EPA, including the use of an air cleaning device to comply with § 129.52, § 129.67, § 129.68(b)(2) and (c)(2), § 129.73 or § 129.77.
(b) New source performance standards. Sources covered by new source performance standards which are more stringent than those contained in this chapter shall comply with those standards in lieu of the standards found in this chapter.
(c) Demonstration of compliance. Test methods and procedures used to monitor compliance with the emission requirements of this section are those specified in Chapter 139 (relating to sampling and testing).
(d) Records. The owner or operator of a facility or source subject to the VOC emission limitations and control requirements in this chapter shall keep records to demonstrate compliance with the applicable limitation or control requirement.
(1) The records shall provide sufficient data and calculations to clearly demonstrate that the emission limitations or control requirements are met. Data or information required to determine compliance with an applicable limitation shall be recorded and maintained in a time frame consistent with the averaging period of the standard.
(2) The records shall be retained at least 2 years and shall be made available to the Department on request.
(3) An owner or operator claiming that a facility or source is exempt from the VOC control provisions of this chapter shall maintain records that clearly demonstrate to the Department that the facility or source is not subject to the VOC emission limitations or control requirements.
§ 129.77. Control of emissions from the use or application of adhesives, sealants, primers and solvents.
(a) This section applies to the owner or operator of a facility that uses or applies one or more of the following at the facility on or after January 1, 2012:
(1) An adhesive, sealant, adhesive primer or sealant primer subject to the VOC content limits in Table V.
(2) An adhesive or sealant product applied to the listed substrate subject to the VOC content limits in Table VI.
(3) A surface preparation solvent or cleanup solvent.
(b) On or after January 1, 2012, an owner or operator of a facility may not use or apply at the facility an adhesive, sealant, adhesive primer or sealant primer that exceeds the applicable VOC content limit in Table V or VI, except as provided elsewhere in this section.
(c) On or after January 1, 2012, an owner or operator of a facility may not use or apply at the facility a surface preparation or cleanup solvent that exceeds the applicable VOC content limit or composite partial vapor pressure requirements of this section, except as provided elsewhere in this section.
(d) The VOC content limits in Table VI for adhesives or sealants applied to particular substrates apply as follows:
(1) If an owner or operator of a facility uses or applies at the facility an adhesive or sealant subject to a specific VOC content limit in Table V, the specific limit is applicable rather than the adhesive-to-substrate limit in Table VI.
(2) If an owner or operator of a facility uses or applies at the facility an adhesive to bond dissimilar substrates together, the applicable substrate category with the highest VOC content limit is the limit for this use.
(e) An owner or operator of a facility subject to this section using or applying a surface preparation solvent or cleanup solvent at the facility may not:
(1) Except as provided in paragraph (2) for single-ply roof membrane, use materials containing VOCs for surface preparation, unless the VOC content of the surface preparation solvent is less than 70 grams per liter of material or 0.6 pound of VOC per gallon of material.
(2) Use materials containing VOCs for surface preparation or cleanup when applying single-ply roof membrane, unless the composite partial vapor pressure, excluding water and exempt compounds, of the surface preparation solvent or cleanup solvent is less than or equal to 45 mm mercury at 20° C.
(3) Except as provided in subsection (f), use cleanup solvent materials containing VOCs for the removal of adhesives, sealants, adhesive primers or sealant primers from surfaces, other than from the parts of spray application equipment, unless the composite partial vapor pressure of the solvent is less than or equal to 45 mm mercury at 20° C.
(f) Removal of an adhesive, sealant, adhesive primer or sealant primer from the parts of spray application equipment shall be performed by one or more of the following methods:
(1) Using an enclosed cleaning system, or an equivalent cleaning system as determined by the test method identified in subsection (z).
(2) Using a solvent with a VOC content less than or equal to 70 grams of VOC per liter of material or 0.6 pound of VOC per gallon of material.
(3) Soaking parts containing dried adhesive in a solvent if the composite partial vapor pressure of the solvent, excluding water and exempt compounds, is less than or equal to 9.5 mm mercury at 20° C and the parts and solvent are in a closed container that remains closed except when adding parts to or removing parts from the container.
(g) An owner or operator of a facility using or applying at the facility an adhesive, sealant, adhesive primer, sealant primer, surface preparation solvent or cleanup solvent subject to the VOC content limits of this section may comply with the requirements of this section through the use of add-on air pollution control equipment if the following requirements are met:
(1) The VOC emissions from the use of all noncomplying as applied adhesives, sealants, adhesive primers, sealant primers, surface preparation solvents and cleanup solvents subject to this section are reduced by an overall efficiency of at least 85%, by weight.
(i) The capture efficiency of the system shall be determined in accordance with subsection (y)(1).
(ii) The control efficiency of the system shall be determined in accordance with subsection (y)(2).
(2) The combustion temperature is continuously monitored and recorded daily if a thermal incinerator is operated.
(3) Inlet and exhaust gas temperatures are continuously monitored and recorded daily if a catalytic incinerator is operated.
(4) Control device efficiency is monitored continuously and recorded daily if a carbon absorber or control device other than a thermal or catalytic incinerator is operated.
(5) Operation records sufficient to demonstrate compliance with the requirements of this section are maintained in accordance with subsections (o), (p) and (q).
(6) The following information is also recorded and maintained:
(i) Daily records of the volume used each day of each noncomplying as applied adhesive, sealant, adhesive primer, sealant primer, surface preparation solvent and cleanup solvent.
(ii) Daily records of the hours of operation of the add-on air pollution control equipment.
(iii) Records of all maintenance performed on the add-on air pollution control equipment, including the date and type of maintenance.
(7) The control equipment is approved, in writing, by the Department in an operating permit.
(8) The owner or operator of a facility that intends to comply with this section using add-on air pollution control equipment may apply to the Department for an extension to the compliance date specified in subsections (a)—(c).
(i) The Department will approve the extension request if the request meets the requirements in subparagraph (ii).
(ii) The extension request must:
(A) Be received, in writing, by January 1, 2012.
(B) Include the date by which a permit application or request for plan approval will be submitted.
(C) Demonstrate to the Department's satisfaction that an extension is necessary.
(iii) An extension will be automatically revoked if the recipient fails to comply with its terms by the dates specified in it.
(h) An owner or operator of a facility subject to this section shall store or dispose of all absorbent materials, including cloth or paper, which are moistened with adhesives, sealants, primers, surface preparation solvents or cleanup solvents subject to this section, in nonabsorbent containers at the facility that are kept closed except when placing materials in or removing materials from the container.
(i) An owner or operator of a facility subject to this section may not solicit, require or specify the use or application of an adhesive, sealant, adhesive primer, sealant primer, surface preparation solvent or cleanup solvent if the use or application would result in a violation of this section, unless the emissions are controlled through the use of add-on air pollution control equipment as specified in subsection (g). The prohibition of this subsection applies to all written or oral contracts created on or after January 1, 2012, under which an adhesive, sealant, adhesive primer, sealant primer, surface preparation solvent or cleanup solvent subject to this section is to be used or applied at a facility in this Commonwealth.
(j) An owner or operator of a facility subject to this section who uses or applies an adhesive, sealant, adhesive primer or sealant primer subject to this section may not add solvent to the adhesive, sealant, adhesive primer or sealant primer in an amount in excess of the manufacturer's recommendation for application, if this addition causes the adhesive, sealant, adhesive primer or sealant primer to exceed the applicable VOC content limit listed in Table V or VI, unless the emissions are controlled through the use of add-on air pollution control equipment as specified in subsection (g).
(k) This section does not apply to the use or application of the following compounds or products:
(1) Adhesives, sealants, adhesive primers or sealant primers being tested or evaluated in a research and development, quality assurance or analytical laboratory, if records are maintained as required in subsections (p) and (q).
(2) Adhesives, sealants, adhesive primers or sealant primers that are subject to § 129.73 (relating to aerospace manufacturing and rework) or Chapter 130, Subchapter B or C (relating to consumer products; and architectural and industrial maintenance coatings).
(3) Adhesives and sealants that contain less than 20 grams of VOC per liter of adhesive or sealant, less water and less exempt compounds, as applied.
(4) Cyanoacrylate adhesives.
(5) Adhesives, sealants, adhesive primers or sealant primers that are sold or supplied by the manufacturer or supplier in containers with a net volume of 16 fluid ounces or less, or a net weight of 1 pound or less, except plastic cement welding adhesives and contact adhesives.
(6) Contact adhesives that are sold or supplied by the manufacturer or supplier in containers with a net volume of 1 gallon or less.
(l) This section does not apply to the use of adhesives, sealants, adhesive primers, sealant primers, surface preparation solvents or cleanup solvents in the following operations:
(1) Tire repair operations, if the label of the adhesive states, ''For tire repair only.''
(2) The assembly, repair and manufacture of aerospace components or undersea-based weapons systems.
(3) The manufacture of medical equipment.
(4) Plaque laminating operations in which adhesives are used to bond clear, polyester acetate laminate to wood with lamination equipment installed prior to July 1, 1992. An owner or operator claiming an exemption under this paragraph shall record and maintain operational records sufficient to demonstrate compliance with this exemption, in accordance with subsections (o)—(q).
(m) This section does not apply if the total VOC emissions from all adhesives, sealants, adhesive primers and sealant primers used or applied at the facility are less than 200 pounds or an equivalent volume, per calendar year. An owner or operator of a facility claiming exemption under this subsection shall record and maintain operational records sufficient to demonstrate compliance with this exemption, in accordance with subsections (o)—(q).
(n) This section does not apply to the use or application of a noncomplying adhesive, sealant, adhesive primer, sealant primer, surface preparation solvent or cleanup solvent if the total volume of noncomplying adhesives, sealants, primers, surface preparation and cleanup solvents used or applied facility-wide does not exceed 55 gallons per calendar year. An owner or operator of a facility claiming exemption under this subsection shall record and maintain operational records sufficient to demonstrate compliance with this exemption, in accordance with subsections (o)—(q).
(o) Except as provided in subsection (p), each owner or operator subject to this section shall maintain records demonstrating compliance with this section, including the following information:
(1) A list of each adhesive, sealant, adhesive primer, sealant primer, surface preparation solvent and cleanup solvent product in use and in storage.
(2) A data sheet or material list which provides the product name, manufacturer identification and use or material application for each product included on the list required under paragraph (1).
(3) The VOC content of each product on the list required under paragraph (1), as supplied.
(4) Catalysts, reducers or other components used and the mix ratio.
(5) The VOC content or vapor pressure of each product on the list required by paragraph (1), as applied, if solvent or other VOC is added to the product before application.
(6) The volume purchased or produced of each product on the list required under paragraph (1).
(7) The monthly volume used or applied as part of a manufacturing process at the facility of each product on the list required under paragraph (1).
(p) For an adhesive, sealant, adhesive primer and sealant primer product subject to the laboratory testing exemption of subsection (k)(1), the person conducting the testing shall make and maintain records of all products used, including the following information:
(1) The product name.
(2) The product category of the material or type of application.
(3) The VOC content of the material.
(q) Records made to determine compliance with this section shall be:
(1) Maintained onsite for 5 years from the date the record is created.
(2) Made available to the Department upon receipt of a written request.
(r) Except as otherwise provided in this section, the VOC and solids content of nonaerosol adhesives (including one-part moisture cure urethane adhesives and silicone adhesives), sealants, adhesive primers, sealant primers, surface preparation solvents and cleanup solvents shall be determined using one of the following:
(1) EPA Reference Method 24, Determination of Volatile Matter Content, Water Content, Density, Volume Solids, and Weight Solids of Surface Coatings, found at 40 CFR 60, Subpart D, Appendix A, including updates and revisions.
(2) SCAQMD Method 304, Determination of Volatile Organic Compounds (VOC) in Various Materials, SCAQMD, 21865 Copley Drive, Diamond Bar, CA 91765 USA, including updates and revisions.
(s) The weight volatile matter content and weight solids content for one-part or multiple part reactive adhesives, except one-part moisture cure urethane adhesives and silicone adhesives, shall be determined using the EPA Reference Method, Determination of Weight Volatile Matter Content and Weight Solids Content of Reactive Adhesives, found at 40 CFR 63, Subpart PPPP, Appendix A, including updates and revisions.
(t) The identity and concentration of exempt organic compounds shall be determined using one of the following:
(1) ASTM D4457, Standard Test Method for Determination of Dichloromethane and 1,1,1-Trichloroethane in Paints and Coatings by Direct Injection into a Gas Chromatograph, ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, P. O. Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959 USA including updates and revisions.
(2) SCAQMD Method 303, Determination of Exempt Compounds, SCAQMD, 21865 Copley Drive, Diamond Bar, CA 91765 USA, including updates and revisions.
(u) The VOC content of a plastic cement welding adhesive or primer shall be determined using SCAQMD Method 316A, Determination of Volatile Organic Compounds (VOC) in Materials Used for Pipes and Fittings, SCAQMD, 21865 Copley Drive, Diamond Bar, CA 91765 USA, including updates and revisions.
(v) To determine if a diluent is a reactive diluent, the percentage of the reactive organic compound that becomes an integral part of the finished material shall be determined using SCAQMD Method 316A, Determination of Volatile Organic Compounds (VOC) in Materials Used for Pipes and Fittings, SCAQMD, 21865 Copley Drive, Diamond Bar, CA 91765 USA, including updates and revisions.
(w) The composite partial vapor pressure of organic compounds in cleaning materials shall be determined by the following procedure:
(1) Quantifying the amount of each compound in the blend using gas chromatographic analysis, using the following methods:
(i) ASTM E260, Standard Practice for Packed Column Gas Chromatography, ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, P. O. Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959 USA, for organic content, including updates and revisions.
(ii) ASTM D3792, Standard Test Method for Water Content of Coatings by Direct Injection Into a Gas Chromatograph, ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, P. O. Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959 USA, for water content, including updates and revisions.
(2) Calculating the composite partial vapor pressure using the following equation:
Where:
PPc = VOC composite partial vapor pressure at 20° C, in mm mercury.
Wi = Weight of the ''i''th VOC compound, in grams, as determined by ASTM E260.
Ww = Weight of water, in grams, as determined by ASTM D3792.
We = Weight of the ''e''th exempt compound, in grams, as determined by ASTM E260.
MWi = Molecular weight of the ''i''th VOC compound, in grams per g-mole, as given in chemical reference literature.
MWw = Molecular weight of water, in grams per g-mole (18 grams per g-mole).
MWe = Molecular weight of the ''e''th exempt compound, in grams per g-mole, as given in chemical reference literature.
VPi = Vapor pressure of the ''i''th VOC compound at 20° C, in mm mercury, as determined by subsection (x).
(x) The vapor pressure of each single component compound shall be determined from one or more of the following:
(1) ASTM D2879, Standard Test Method for Vapor Pressure-Temperature Relationship and Initial Decomposition Temperature of Liquids by Isoteniscope, ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, P. O. Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959 USA, including updates and revisions.
(2) The most recent edition of one or more of the following sources:
(i) Vapour Pressures of Pure Substances, Boublik, Elsevier Scientific Publishing Company, New York.
(ii) Perry's Chemical Engineers' Handbook, Green and Perry, McGraw-Hill Book Company.
(iii) CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics, CRC Press.
(iv) Lange's Handbook of Chemistry, McGraw-Hill Book Company.
(v) Additional sources approved by the SCAQMD or other California air districts.
(y) If air pollution control equipment is used to meet the requirements of this section, the owner or operator shall make both of the following determinations:
(1) The measurement of capture efficiency shall be conducted and reported in accordance with the EPA Technical Document ''Guidelines for Determining Capture Efficiency,'' issued January 9, 1995.
(2) The control efficiency shall be determined in accordance with one of the following:
(i) EPA Reference Method 25, Determination of Total Gaseous Nonmethane Organic Emissions as Carbon, found at 40 CFR 60, Subpart D, Appendix A, including updates and revisions.
(ii) EPA Reference Method 25A, Determination of Total Gaseous Organic Concentration Using a Flame Ionization Analyzer, found at 40 CFR 60, Subpart D, Appendix A, including updates and revisions.
(iii) EPA Reference Method 25B, Determination of Total Gaseous Organic Concentration Using a Nondispersive Infrared Analyzer, found at 40 CFR 60, Subpart D, Appendix A, including updates and revisions.
(iv) CARB Method 100, Procedures for Continuous Gaseous Emission Stack Sampling, California Air Resources Board, 1001 ''I'' Street, Post Office Box 2815, Sacramento, CA 95812 USA, including updates and revisions.
(z) The active and passive solvent losses from the use of an enclosed spray gun cleaning system or equivalent cleaning system, as listed in subsection (f)(1), shall be determined using the SCAQMD method, General Test Method for Determining Solvent Losses from Spray Gun Cleaning Systems, dated October 3, 1989, SCAQMD, 21865 Copley Drive, Diamond Bar, CA 91765 USA, including updates and revisions.
(1) The test solvent for this determination shall be a lacquer thinner with a minimum vapor pressure of 105 mm of mercury at 20° C.
(2) The minimum test temperature shall be 15° C.
(aa) Another test method may be used to determine the VOC or solids content of a product if the request for approval of the test method meets the following requirements:
(1) The request is submitted to the Department in writing.
(2) The request demonstrates that the test method provides results that accurately determine the concentration of VOCs in the product or its emissions.
(3) The Department approves the request in writing.
(bb) For adhesive, sealant, adhesive primer or sealant primer products that do not contain reactive diluents, grams of VOC per liter of product thinned to the manufacturer's recommendation, less water and exempt compounds, shall be calculated according to the following equation:
Grams of VOC per liter of product, as applied =
Ws - Ww - We
Vm - Vw - VeWhere:
Ws = weight of volatile compounds, in grams.
Ww = weight of water, in grams.
We = weight of exempt compounds, in grams.
Vm = volume of material, in liters.
Vw = volume of water, in liters.
Ve = volume of exempt compounds, in liters.
(cc) For adhesive, sealant, adhesive primer or sealant primer products that contain reactive diluents, the VOC content of the product is determined after curing. The grams of VOC per liter of product thinned to the manufacturer's recommendation, less water and exempt compounds, shall be calculated according to the following equation:
Grams of VOC per liter of product, as applied =
Wrs - Wrw - Wre
Vrm - Vrw - VreWhere:
Wrs = weight of volatile compounds not consumed during curing, in grams.
Wrw = weight of water not consumed during curing, in grams.
Wre = weight of exempt compounds not consumed during curing, in grams.
Vrm = volume of material not consumed during curing, in liters.
Vrw = volume of water not consumed during curing, in liters.
Vre = volume of exempt compounds not consumed during curing, in liters.
(dd) For low-solids adhesive, sealant, adhesive primer or sealant primer products, grams of VOC per liter of product thinned to the manufacturer's recommendation, including the volume of water and exempt compounds, shall be calculated according to the following equation:
Grams of VOC per liter of product, as applied =
Ws - Ww - We
VmWhere:
Ws = weight of volatile compounds, in grams.
Ww = weight of water, in grams.
We = weight of exempt compounds, in grams.
Vm = volume of material, in liters.
(ee) Percent VOC by weight shall be calculated according to the following equation:
% VOC by weight = [(Wv/W)] × 100
Where:
Wv = weight of VOCs, in grams.
W = weight of material, in grams.
(ff) To convert from grams per liter (g/l) to pounds per gallon (lb/gal), multiply the result (VOC content) by 8.345 × 10-3 (lb/gal/g/l).
Table V. VOC Content Limits for Adhesives, Sealants, Adhesive Primers and Sealant Primers, As Applied
Adhesive, sealant, adhesive primer or
sealant primer category
VOC content limit (pounds VOC per gallon, less water and exempt compounds)* VOC content limit (grams VOC per liter, less water and exempt compounds)* Adhesives ABS welding 3.3 400 Ceramic tile installation 1.1 130 Computer diskette jacket manufacturing 7.1 850 Contact bond 2.1 250 Cove base installation 1.3 150 CPVC welding 4.1 490 Indoor floor covering installation 1.3 150 Metal to urethane/rubber molding or casting 7.1 850 Multipurpose construction 1.7 200 Nonmembrane roof installation/repair 2.5 300 Outdoor floor covering installation 2.1 250 Perimeter bonded sheet vinyl flooring installation 5.5 660 Plastic cement welding, other than ABS, CPVC or PVC welding 4.3 510 PVC welding 4.3 510 Sheet rubber installation 7.1 850 Single-ply roof membrane installation/ repair 2.1 250 Structural glazing 0.8 100 Thin metal laminating 6.5 780 Tire retread 0.8 100 Waterproof resorcinol glue 1.4 170 Sealants Architectural 2.1 250 Marine deck 6.3 760 Nonmembrane roof installation/repair 2.5 300 Roadway 2.1 250 Single-ply roof membrane 3.8 450 Other 3.5 420 Adhesive Primers Automotive glass 5.8 700 Plastic cement welding 5.4 650 Single-ply roof membrane 2.1 250 Traffic marking tape 1.3 150 Other 2.1 250 Sealant Primers Marine deck 6.3 760 Nonporous architectural 2.1 250 Porous architectural 6.5 775 Other 6.3 750 *The VOC content is determined as the weight of VOC per volume of product, less water and exempt compounds, as specified in subsections (bb) and (cc) or as the weight of VOC per volume of product, as specified in subsection (dd).
Table VI. VOC Content Limits for Adhesive or Sealant Products Applied to Particular Substrates, As Applied
Adhesive or Sealant Products
Applied to the Listed
SubstrateVOC content limit (pounds VOC per gallon, less water and exempt compounds)* VOC content limit (grams VOC per liter, less water and exempt compounds)* Fiberglass 1.7 200 Flexible vinyl 2.1 250 Metal 0.3 30 Porous material 1.0 120 Rubber 2.1 250 Other substrates 2.1 250 *The VOC content is determined as the weight of VOC per volume of product, less water and exempt compounds, as specified in subsections (bb) and (cc) or as the weight of VOC per volume of product, as specified in subsection (dd).
CHAPTER 130. STANDARDS FOR PRODUCTS
Subchapter D. ADHESIVES, SEALANTS, PRIMERS AND SOLVENTS
GENERAL PROVISIONS Sec.
130.701. Applicability. 130.702. Emission standards. 130.703. Exemptions and exceptions. 130.704. Recordkeeping requirements. 130.705. Compliance procedures and test methods. 130.706. Container labeling. 130.707. Product dating. 130.708. Sell-through of products.
GENERAL PROVISIONS § 130.701. Applicability.
(a) Except as provided in § 130.703 (relating to exemptions and exceptions), this subchapter applies to a person who, on or after January 1, 2012, sells, supplies, offers for sale or manufactures for sale for use or application in this Commonwealth one or more of the following products subject to this subchapter:
(1) An adhesive, sealant, adhesive primer or sealant primer product.
(2) An adhesive or sealant product applied to particular substrates.
(3) A surface preparation solvent or cleanup solvent product.
(b) Except as provided in § 130.703, this subchapter applies to a person who, on or after January 1, 2012, uses or applies for compensation within this Commonwealth one or more of the following products subject to this subchapter:
(1) An adhesive, sealant, adhesive primer or sealant primer product.
(2) An adhesive or sealant product applied to particular substrates.
(3) A surface preparation solvent or cleanup solvent product.
§ 130.702. Emission standards.
(a) Except as provided in § 130.703 (relating to exemptions and exceptions), a person may not sell, supply, offer for sale or manufacture for sale for use or application in this Commonwealth one or more of the following products:
(1) An adhesive, sealant, adhesive primer or sealant primer product manufactured on or after January 1, 2012, which contains VOCs in excess of the applicable VOC content limit specified in Table I.
(2) An adhesive or sealant product manufactured on or after January 1, 2012, if it is sold, supplied, offered for sale or manufactured to be applied in this Commonwealth to a substrate listed in Table II and it contains VOCs in excess of the applicable VOC content limit specified in Table II.
(b) Except as provided in § 130.703, a person may not use or apply for compensation within this Commonwealth one or more of the following products:
(1) An adhesive, sealant, adhesive primer or sealant primer product manufactured on or after January 1, 2012, which contains VOCs in excess of the applicable VOC content limit specified in Table I.
(2) An adhesive or sealant product manufactured on or after January 1, 2012, applied to a substrate listed in Table II if the product contains VOCs in excess of the applicable VOC content limit specified in Table II.
(c) On and after January 1, 2012, the VOC content limits in Table II for adhesives or sealants applied to particular substrates apply as follows:
(1) If a person uses or applies an adhesive or sealant subject to a specific VOC content limit in Table I, the specific limit is applicable rather than the adhesive-to-substrate limit in Table II.
(2) If a person uses or applies an adhesive to bond dissimilar substrates together, the applicable substrate category with the highest VOC content is the limit for this use.
(d) On and after January 1, 2012, a person subject to this subchapter using or applying a surface preparation solvent or cleanup solvent may not:
(1) Except as provided in paragraph (2) for single-ply roof membrane, use materials containing VOCs for surface preparation, unless the VOC content of the surface preparation solvent is less than 70 grams per liter of material or 0.6 pound of VOC per gallon of material.
(2) If a surface preparation solvent is used in applying single-ply roof membrane, use materials containing VOCs for surface preparation, unless the composite partial vapor pressure, excluding water and exempt compounds, of the surface preparation solvent is less than or equal to 45 mm mercury at 20° C.
(3) Except as provided in subsection (e), use materials containing VOCs for the removal of adhesives, sealants or adhesive or sealant primers from surfaces, other than from the parts of spray application equipment, unless the composite partial vapor pressure of the solvent used is less than or equal to 45 mm mercury at 20° C.
(e) On and after January 1, 2012, the removal of an adhesive, sealant, adhesive primer or sealant primer from the parts of spray application equipment shall be performed by one or more of the following methods:
(1) Using an enclosed cleaning system or equivalent cleaning system, as determined by the test method identified in § 130.705(h) (relating to compliance procedures and test methods).
(2) Using a solvent with a VOC content less than or equal to 70 grams of VOC per liter of material or 0.6 pound of VOC per gallon of material.
(3) Soaking parts containing dried adhesive in a solvent if the composite partial vapor pressure of the solvent, excluding water and exempt compounds, is less than or equal to 9.5 mm mercury at 20° C and the parts and solvent are in a closed container that remains closed except when adding parts to or removing parts from the container.
(f) On and after January 1, 2012, a person who uses or applies adhesives, sealants, adhesive primers, sealant primers, surface preparation solvents or cleanup solvents subject to this subchapter shall store or dispose of all absorbent materials, including cloth or paper, which are moistened with adhesives, sealants, primers or solvents subject to this subchapter, in nonabsorbent containers at the facility or location of use that are kept closed except when placing materials in or removing materials from the container.
(g) A person may not solicit, require or specify the use or application of an adhesive, sealant, adhesive primer, sealant primer, surface preparation solvent or cleanup solvent if the use or application would result in a violation of this subchapter. The prohibition of this subsection applies to all written or oral contracts created on or after January 1, 2012, under which an adhesive, sealant, adhesive primer, sealant primer, surface preparation solvent or cleanup solvent subject to this subchapter is to be used or applied at a location in this Commonwealth.
(h) On and after January 1, 2012, a person who, for compensation, uses or applies an adhesive, sealant, adhesive primer or sealant primer in this Commonwealth may not add solvent to the adhesive, sealant, adhesive primer or sealant primer in an amount in excess of the manufacturer's recommendation for application, if this addition causes the adhesive, sealant, adhesive primer or sealant primer to exceed the applicable VOC content limit listed in Table I or II.
Table I. VOC Content Limits for Adhesives, Sealants, Adhesive Primers and Sealant Primers, As Applied
Adhesive, sealant, adhesive primer or sealant primer category VOC content limit (pounds VOC per gallon, less water and exempt compounds)* VOC content limit (grams VOC per liter, less water and exempt compounds)* Adhesives ABS welding 3.3 400 Ceramic tile installation 1.1 130 Computer diskette jacket manufacturing 7.1 850 Contact bond 2.1 250 Cove base installation 1.3 150 CPVC welding 4.1 490 Indoor floor covering installation 1.3 150 Metal to urethane/rubber molding or casting 7.1 850 Multipurpose construction 1.7 200 Nonmembrane roof installation/repair 2.5 300 Outdoor floor covering installation 2.1 250 Perimeter bonded sheet vinyl flooring installation 5.5 660 Plastic cement welding, other than ABS, CPVC or PVC welding 4.3 510 PVC welding 4.3 510 Sheet rubber installation 7.1 850 Single-ply roof membrane installation/ repair 2.1 250 Structural glazing 0.8 100 Thin metal laminating 6.5 780 Tire retread 0.8 100 Waterproof resorcinol glue 1.4 170 Sealants Architectural 2.1 250 Marine deck 6.3 760 Nonmembrane roof installation/repair 2.5 300 Roadway 2.1 250 Single-ply roof membrane 3.8 450 Other 3.5 420 Adhesive Primers Automotive glass 5.8 700 Plastic cement welding 5.4 650 Single-ply roof membrane 2.1 250 Traffic marking tape 1.3 150 Other 2.1 250 Sealant Primers Marine deck 6.3 760 Nonporous architectural 2.1 250 Porous architectural 6.5 775 Other 6.3 750 *The VOC content is determined as the weight of VOC per volume of product, less water and exempt compounds, as specified in § 130.705(j) and (k) or as the weight of VOC per volume of product, as specified in § 130.705(l).
Table II. VOC Content Limits for Adhesive or Sealant Products Applied to Particular Substrates, As Applied
Adhesive or Sealant Products
Applied to the Listed SubstrateVOC content limit (pounds VOC per gallon, less water and exempt compounds)* VOC content limit (grams VOC per liter, less water and exempt compounds)* Fiberglass 1.7 200 Flexible vinyl 2.1 250 Metal 0.3 30 Porous material 1.0 120 Rubber 2.1 250 Other substrates 2.1 250 *The VOC content is determined as the weight of VOC per volume of product, less water and exempt compounds, as specified in § 130.705(j) and (k) or as the weight of VOC per volume of product, as specified in § 130.705(l).
§ 130.703. Exemptions and exceptions.
(a) This subchapter does not apply to the use, application, sale, supply, offer for sale or manufacture for sale for use in this Commonwealth of the following compounds or products:
(1) Adhesives, sealants, adhesive primers or sealant primers being tested or evaluated in a research and development, quality assurance or analytical laboratory, if records are maintained as required under § 130.704 (relating to recordkeeping requirements).
(2) Adhesives, sealants, adhesive primers or sealant primers that are subject to § 129.73 (relating to aerospace manufacturing and rework) or Chapter 130, Subchapter B or C (relating to consumer products; and architectural and industrial maintenance coatings).
(3) Adhesives and sealants that contain less than 20 grams of VOC per liter of adhesive or sealant, less water and less exempt compounds, as applied.
(4) Cyanoacrylate adhesives.
(5) Adhesives, sealants, adhesive primers or sealant primers that are sold or supplied by the manufacturer or supplier in containers with a net volume of 16 fluid ounces or less, or a net weight of 1 pound or less, except plastic cement welding adhesives and contact adhesives.
(6) Contact adhesives that are sold or supplied by the manufacturer or supplier in containers with a net volume of 1 gallon or less.
(b) This subchapter does not apply to the use, application, sale, supply, offer for sale or manufacture for sale for use in this Commonwealth of adhesives, sealants, adhesive primers, sealant primers, surface preparation solvents or cleanup solvents in the following operations:
(1) Tire repair operations, if the label of the adhesive states, ''For tire repair only.''
(2) The assembly, repair and manufacture of aerospace components or undersea-based weapons systems.
(3) The manufacture of medical equipment.
(4) Plaque laminating operations in which adhesives are used to bond clear, polyester acetate laminate to wood with lamination equipment installed prior to July 1, 1992. A person claiming an exemption under this paragraph shall record and maintain operational records sufficient to demonstrate compliance with this exemption, in accordance with § 130.704.
(c) This subchapter does not apply to an adhesive, sealant, adhesive primer or sealant primer product if the manufacturer or distributor of the product makes and keeps records demonstrating both of the following:
(1) The adhesive, sealant, adhesive primer or sealant primer product is intended for shipment and use outside of this Commonwealth.
(2) The manufacturer or distributor has taken reasonably prudent precautions to assure that the adhesive, sealant, adhesive primer or sealant primer product is not distributed to or within this Commonwealth.
(d) The exemption in subsection (c) does not apply to an adhesive, sealant, adhesive primer or sealant primer product that is sold, supplied or offered for sale to a retail outlet in this Commonwealth.
(e) This subchapter does not apply to an adhesive, sealant, adhesive primer, sealant primer, surface preparation solvent or cleanup solvent product that is sold or supplied for use or application as part of a manufacturing process at a facility subject to the requirements of § 129.77 (relating to control of emissions from the use or application of adhesives, sealants, primers and solvents).
(f) This subchapter does not apply to an adhesive, sealant, adhesive primer, sealant primer, surface preparation solvent or cleanup solvent used or applied in either of the following situations:
(1) At a private residence for a noncommercial purpose.
(2) By a person who is not seeking compensation.
§ 130.704. Recordkeeping requirements.
(a) On and after January 1, 2012, a person who sells, supplies, offers for sale or manufactures for sale for use in this Commonwealth an adhesive, sealant, adhesive primer, sealant primer, surface preparation solvent or cleanup solvent product subject to this subchapter shall maintain records demonstrating compliance with this subchapter, including the following information:
(1) A data sheet or material list which provides the material name, manufacturer identification and material application for each product.
(2) The VOC content of each product, as supplied.
(3) The number of gallons of product sold in this Commonwealth.
(b) On and after January 1, 2012, a person who uses or applies an adhesive, sealant, adhesive primer, sealant primer, surface preparation solvent or cleanup solvent product subject to this subchapter shall maintain records demonstrating compliance with this subchapter, including the following information:
(1) A list of each adhesive, sealant, adhesive primer, sealant primer, surface preparation solvent and cleanup solvent product in use and in storage.
(2) A data sheet or material list which provides the product name, manufacturer identification and use or material application for each product included on the list required under paragraph (1).
(3) The VOC content of each product on the list required under paragraph (1), as supplied.
(4) Catalysts, reducers or other components used and the mix ratio.
(5) The VOC content or vapor pressure of each product on the list required under paragraph (1), as applied, if solvent or other VOC is added to the product before application.
(6) The monthly volume used of each product on the list required under paragraph (1).
(c) For an adhesive, sealant, adhesive primer and sealant primer product subject to the laboratory testing exemption of § 130.703(a)(1) (relating to exemptions and exceptions), on and after January 1, 2012, the person conducting the testing shall make and maintain records of all materials used, including the following information:
(1) The product name.
(2) The product category of the material or type of application.
(3) The VOC content of the material.
(d) Records made to determine compliance with this subchapter shall be:
(1) Maintained for 5 years from the date the record is created.
(2) Made available to the Department upon receipt of a written request.
§ 130.705. Compliance procedures and test methods.
(a) Except as otherwise provided in this section, the VOC and solids content of nonaerosol adhesives (including one-part moisture cure urethane adhesives and silicone adhesives), sealants, adhesive primers, sealant primers, surface preparation solvents and cleanup solvents shall be determined using one of the following:
(1) EPA Reference Method 24, Determination of Volatile Matter Content, Water Content, Density, Volume Solids, and Weight Solids of Surface Coatings, found at 40 CFR 60, Subpart D, Appendix A, including updates and revisions.
(2) SCAQMD Method 304, Determination of Volatile Organic Compounds (VOC) in Various Materials, SCAQMD, 21865 Copley Drive, Diamond Bar, CA 91765 USA, including updates and revisions.
(b) The weight volatile matter content and weight solids content for one-part or multiple part reactive adhesives, except one-part moisture cure urethane adhesives and silicone adhesives, shall be determined using the EPA Reference Method, Determination of Weight Volatile Matter Content and Weight Solids Content of Reactive Adhesives, found at 40 CFR 63, Subpart PPPP, Appendix A, including updates and revisions.
(c) The identity and concentration of exempt organic compounds shall be determined using one of the following:
(1) ASTM D4457, Standard Test Method for Determination of Dichloromethane and 1,1,1-Trichloroethane in Paints and Coatings by Direct Injection into a Gas Chromatograph, ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, Post Office Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959 USA, including updates and revisions.
(2) SCAQMD Method 303, Determination of Exempt Compounds, SCAQMD, 21865 Copley Drive, Diamond Bar, CA 91765 USA, including updates and revisions.
(d) The VOC content of a plastic cement welding adhesive or primer shall be determined using SCAQMD Method 316A, Determination of Volatile Organic Compounds (VOC) in Materials Used for Pipes and Fittings, SCAQMD, 21865 Copley Drive, Diamond Bar, CA 91765 USA, including updates and revisions.
(e) To determine if a diluent is a reactive diluent, the percentage of the reactive organic compound that becomes an integral part of the finished material shall be determined using SCAQMD Method 316A, Determination of Volatile Organic Compounds (VOC) in Materials Used for Pipes and Fittings, SCAQMD, 21865 Copley Drive, Diamond Bar, CA 91765 USA, including updates and revisions.
(f) The composite partial vapor pressure of organic compounds in cleaning materials shall be determined by the following procedure:
(1) Quantifying the amount of each compound in the blend using gas chromatographic analysis, using the following methods:
(i) ASTM E260, Standard Practice for Packed Column Gas Chromatography, ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, Post Office Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959 USA, for organic content, including updates and revisions.
(ii) ASTM D3792, Standard Test Method for Water Content of Coatings by Direct Injection Into a Gas Chromatograph, ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, Post Office Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959 USA, for water content, including updates and revisions.
(2) Calculating the composite partial vapor pressure using the following equation:
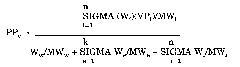
Where:
PPc = VOC composite partial vapor pressure at 20° C, in mm mercury.
Wi = Weight of the ''i''th VOC compound, in grams, as determined by ASTM E260.
Ww = Weight of water, in grams, as determined by ASTM D3792.
We = Weight of the ''e''th exempt compound, in grams, as determined by ASTM E260.
MWi = Molecular weight of the ''i''th VOC compound, in grams per g-mole, as given in chemical reference literature.
MWw = Molecular weight of water, in grams per g-mole (18 grams per g-mole).
MWe = Molecular weight of the ''e''th exempt compound, in grams per g-mole, as given in chemical reference literature.
VPi = Vapor pressure of the ''i''th VOC compound at 20° C, in mm mercury, as determined by subsection (f).
(g) The vapor pressure of each single component compound shall be determined from one or more of the following:
(1) ASTM D2879, Standard Test Method for Vapor Pressure-Temperature Relationship and Initial Decomposition Temperature of Liquids by Isoteniscope, ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, P. O. Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959 USA, including updates and revisions.
(2) The most recent edition of one or more of the following sources:
(i) Vapour Pressures of Pure Substances, Boublik, Elsevier Scientific Publishing Company, New York.
(ii) Perry's Chemical Engineers' Handbook, Green and Perry, McGraw-Hill Book Company.
(iii) CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics, CRC Press.
(iv) Lange's Handbook of Chemistry, McGraw-Hill Book Company.
(v) Additional sources approved by the SCAQMD or other California air districts.
(h) The active and passive solvent losses from the use of an enclosed spray gun cleaning system or equivalent cleaning system, as listed in § 130.702(e)(1) (relating to emission standards), shall be determined using the SCAQMD method, General Test Method for Determining Solvent Losses from Spray Gun Cleaning Systems, dated October 3, 1989, SCAQMD, 21865 Copley Drive, Diamond Bar, CA 91765 USA, including updates and revisions.
(1) The test solvent for this determination shall be a lacquer thinner with a minimum vapor pressure of 105 mm of mercury at 20° C.
(2) The minimum test temperature shall be 15° C.
(i) Another test method may be used to determine the VOC or solids content of a product if the request for approval of the test method meets the following requirements:
(A) The request is submitted to the Department in writing.
(B) The request demonstrates that the test method provides results that accurately determine the concentration of VOCs in the product or its emissions.
(C) The Department approves the request in writing.
(j) For adhesive, sealant or primer products that do not contain reactive diluents, grams of VOC per liter of product thinned to the manufacturer's recommendation, less water and exempt compounds, shall be calculated according to the following equation:
Grams of VOC per liter of product, as applied =
Ws - Ww - We
Vm - Vw - VeWhere:
Ws = weight of volatile compounds, in grams.
Ww = weight of water, in grams.
We = weight of exempt compounds, in grams.
Vm = volume of material, in liters.
Vw = volume of water, in liters.
Ve = volume of exempt compounds, in liters.
(k) For adhesive, sealant or primer products that contain reactive diluents, the VOC content of the product is determined after curing. The grams of VOC per liter of product thinned to the manufacturer's recommendation, less water and exempt compounds, shall be calculated according to the following equation:
Grams of VOC per liter of product, as applied =
Wrs - Wrw - Wre
Vrm - Vrw - VreWhere:
Wrs = weight of volatile compounds not consumed during curing, in grams.
Wrw = weight of water not consumed during curing, in grams.
Wre = weight of exempt compounds not consumed during curing, in grams.
Vrm = volume of material not consumed during curing, in liters.
Vrw = volume of water not consumed during curing, in liters.
Vre = volume of exempt compounds not consumed during curing, in liters.
(l) For low-solids adhesive, sealant or primer products, grams of VOC per liter of product thinned to the manufacturer's recommendation, including water and exempt compounds, shall be calculated according to the following equation:
Grams of VOC per liter of product, as applied =
Ws - Ww - We
VmWhere:
Ws = weight of volatile compounds, in grams.
Ww = weight of water, in grams.
We = weight of exempt compounds, in grams.
Vm = volume of material, in liters.
(m) Percent VOC by weight shall be calculated according to the following equation:
% VOC by weight = [(Wv/W)] × 100
Where:
Wv = weight of VOCs in grams.
W = weight of material in grams.
(n) To convert from grams per liter (g/l) to pounds per gallon (lb/gal), multiply the result (VOC content) by 8.345 × 10-3 (lb/gal/g/l).
§ 130.706. Container labeling.
On and after January 1, 2012, each manufacturer of an adhesive, sealant, adhesive primer or sealant primer product subject to this subchapter shall display the following information on the product container or label:
(1) A statement of the manufacturer's recommendation regarding thinning, reducing or mixing of the product, except that:
(i) This requirement does not apply to the thinning of a product with water.
(ii) If thinning of the product prior to use is not necessary, the recommendation must specify that the product is to be applied without thinning.
(2) The maximum or the actual VOC content of the product as supplied, displayed as one of the following:
(i) Weight of VOC per volume of product, less water and exempt compounds, calculated in accordance with § 130.705(j) and (k) (relating to compliance procedures and test methods).
(ii) Weight of VOC per volume of product, calculated in accordance with § 130.705(l).
(3) The maximum or the actual VOC content of the product as applied, which includes the manufacturer's maximum recommendation for thinning, displayed as one of the following:
(i) Weight of VOC per volume of product, less water and exempt compounds, calculated in accordance with § 130.705(j) and (k).
(ii) Weight of VOC per volume of product, calculated in accordance with § 130.705(l).
§ 130.707. Product dating.
(a) Product dating requirements.
(1) Each manufacturer of an adhesive, sealant, adhesive primer, sealant primer, surface preparation solvent or cleanup solvent product subject to this subchapter shall clearly display on each product container or package, the day, month and year on which the product was manufactured, or a code indicating that date.
(2) A manufacturer who uses the following code to indicate the date of manufacture will not be subject to the requirements of subsection (b)(1), if the code is represented separately from other codes on the product container so that it is easily recognizable:
YY DDD = Year Year Day Day Day
Where,
YY = Two digits representing the year in which the product was manufactured
DDD = Three digits representing the day of the year on which the product was manufactured, with ''001'' representing the first day of the year, ''002'' representing the second day of the year, and so forth (that is, the ''Julian date'').
(3) The product date or date-code required by this section must be displayed on each product container or package before the product is sold, supplied or offered for sale in this Commonwealth.
(4) The date or date-code information must be located on the container or inside the cover or cap so that it is readily observable or obtainable (by simply removing the cover or cap) without irreversibly disassembling a part of the container or packaging.
(5) For the purposes of this subsection, information may be displayed on the bottom of a container as long as it is clearly legible without removing any product packaging.
(6) The requirements of this subsection do not apply to products containing either of the following:
(i) No VOCs.
(ii) VOCs at 0.10% by weight or less.
(b) Additional product dating requirements.
(1) If a manufacturer uses a code other than the code described in subsection (a)(2) indicating the date of manufacture for an adhesive, sealant, adhesive primer, sealant primer, surface preparation solvent or cleanup solvent product subject to this subchapter, the manufacturer must file an explanation of the date portion of the code with the Department before the product is sold, supplied or offered for sale in this Commonwealth.
(2) If a manufacturer changes a code indicating the date of manufacture for a product subject to paragraph (1), the manufacturer must file an explanation of the modified code with the Department before products displaying the modified code are sold, supplied or offered for sale in this Commonwealth.
(3) A person may not erase, alter, deface or otherwise remove or make illegible a date or code indicating the date of manufacture from a regulated product container without the express authorization of the manufacturer.
(4) Date code explanations for codes indicating the date of manufacture are public information and may not be claimed as confidential.
§ 130.708. Sell-through of products.
(a) Sell-through period. An adhesive, sealant, adhesive primer, sealant primer, surface preparation solvent or cleanup solvent product subject to this subchapter and manufactured prior to January 1, 2012, may be sold, supplied or offered for sale on or after January 1, 2012.
(b) No date or date code. This section does not apply to an adhesive, sealant, adhesive primer, sealant primer, surface preparation solvent or cleanup solvent product subject to this subchapter that does not display on the product container or package the date on which the product was manufactured, or a code indicating the date, in accordance with § 130.707 (relating to product dating).
[Pa.B. Doc. No. 10-2456. Filed for public inspection December 23, 2010, 9:00 a.m.]
No part of the information on this site may be reproduced for profit or sold for profit.This material has been drawn directly from the official Pennsylvania Bulletin full text database. Due to the limitations of HTML or differences in display capabilities of different browsers, this version may differ slightly from the official printed version.